


Introduction:
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on financial leverage, where we explore the concept’s significance, practical applications, real-life examples, and critical analysis. Whether you’re a business owner, investor, or finance enthusiast, understanding financial leverage is essential for optimizing growth and maximizing profitability. In this blog post, we will delve into the world and Indian context of financial leverage, showcasing numerous real-life examples, case studies, and numerical illustrations. So, let’s dive in and unlock the potential of financial leverage!
Index:
1. Introduction
2. Understanding Financial Leverage
3. Types of Financial Leverage
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Financial Leverage
5. Real-Life Examples of Financial Leverage in the World Context
5.1 Case Study: Apple Inc.
5.2 Case Study: Amazon.com Inc.
5.3 Case Study: The Walt Disney Company
6. Financial Leverage in the Indian Context
6.1 Case Study: Tata Motors
6.2 Case Study: Reliance Industries Limited
6.3 Case Study: Infosys Limited
7. Numerical Analysis: Calculating Financial Leverage Ratios
8. Applications of Financial Leverage
8.1 Investing in Stocks and Bonds
8.2 Starting or Expanding a Business
8.3 Mergers and Acquisitions
9. Critical Analysis of Financial Leverage
10. Conclusion
2- Understanding Financial Leverage:
Financial leverage is a powerful tool that allows individuals and businesses to utilize borrowed funds to make investments and potentially generate higher returns. It involves using debt to finance assets or projects with the expectation that the returns generated will exceed the cost of borrowing. By employing financial leverage, individuals or businesses can amplify their potential profits and accelerate their growth.
To understand financial leverage, it is crucial to grasp its formula and components. The most common ratio used to measure financial leverage is the debt-to-equity ratio, which compares the amount of debt a company has taken on to its shareholders’ equity. A high debt-to-equity ratio indicates that a company relies heavily on borrowed funds, while a low ratio signifies a more conservative financing approach.
The significance of financial leverage lies in its ability to magnify both gains and losses. When investments perform well, the returns are higher than the cost of borrowing, leading to increased profits and enhanced returns on equity. However, if the investments underperform, the higher interest payments on the debt can become a burden, potentially resulting in financial distress.
Financial leverage is a crucial factor in decision-making, as it involves balancing risk and reward. It allows individuals and businesses to optimize their capital structure by determining the right mix of debt and equity financing. Different industries and business models have varying optimal leverage levels, and understanding the specific needs and circumstances of a venture is crucial in determining the appropriate level of leverage.
By strategically employing financial leverage, companies can enhance their ability to invest in growth opportunities, such as expanding operations, developing new products, or entering new markets. However, it is essential to assess the potential risks associated with financial leverage, including interest rate fluctuations, credit risk, and the company’s ability to generate sufficient cash flow to cover debt obligations.
In summary, financial leverage is a strategy that enables individuals and businesses to use borrowed funds to finance investments and potentially achieve higher returns. It involves balancing the benefits of amplifying profits with the risks of increased financial obligations. Understanding financial leverage is vital for making informed decisions regarding capital structure and optimizing growth and profitability.
Remember to check out the rest of the blog post for further insights into the different types of financial leverage, real-life examples, case studies, and practical applications in both global and Indian contexts.
3- Types of Financial Leverage:
Financial leverage can be categorized into three main types: operating leverage, financial leverage, and combined leverage. Each type has its unique characteristics and implications, and understanding them is crucial for effectively utilizing financial leverage in different scenarios.
1. Operating Leverage:
Operating leverage refers to the use of fixed operating costs, such as rent, salaries, and depreciation, to increase the potential returns on investment. It primarily focuses on leveraging the revenue-generating capabilities of a company. By having a higher proportion of fixed costs in the cost structure, a company can achieve economies of scale and generate higher profits when sales increase.
For example, a manufacturing company that invests in expensive machinery and factories incurs significant fixed costs. As sales volume rises, the fixed costs remain the same, leading to higher profit margins. However, if sales decline, the fixed costs become a burden, resulting in lower profitability.
2. Financial Leverage:
Financial leverage involves using debt to finance investments and increase the potential return on equity. It focuses on the capital structure of a company, specifically the proportion of debt to equity. By employing financial leverage, companies can amplify their returns by leveraging borrowed funds.
The key financial leverage ratio used to assess the proportion of debt in relation to equity is the debt-to-equity ratio. A high debt-to-equity ratio indicates a higher level of financial leverage, implying that a company relies more on borrowed funds for financing.
It’s important to note that while financial leverage has the potential to increase returns, it also amplifies risks. Higher debt levels increase interest expenses, and if the investments underperform, the burden of debt servicing becomes more challenging. Careful analysis and risk management are essential when employing financial leverage.
3. Combined Leverage:
Combined leverage is a combination of operating leverage and financial leverage. It considers both the fixed operating costs and the proportion of debt in the capital structure. By understanding the interplay between operating and financial leverage, companies can optimize their overall leverage position.
Combined leverage allows companies to evaluate the impact of changes in sales volume on their profitability. It helps in assessing the breakeven point, analyzing the sensitivity of profits to changes in sales, and making informed decisions regarding the level of debt and fixed costs in the capital structure.
Understanding the different types of financial leverage is crucial for decision-making, as each type has its own implications and considerations. Depending on the industry, business model, and growth objectives, companies can strategically employ a combination of these leverages to achieve their financial goals.
By carefully analyzing the risks and rewards associated with each type of leverage, businesses can strike a balance that maximizes profitability while mitigating potential downsides. Moreover, regular monitoring and adjustment of leverage levels based on changing market conditions and business dynamics are essential for long-term financial sustainability.
4- Advantages and Disadvantages of Financial Leverage:
Financial leverage can offer several advantages to individuals and businesses, but it also carries certain disadvantages that need to be carefully considered. Understanding both sides of the equation is crucial for making informed decisions regarding the use of financial leverage.
Advantages of Financial Leverage:
1. Increased Return on Equity: By using borrowed funds to finance investments, financial leverage has the potential to amplify returns on equity. When the returns generated from the investments exceed the cost of borrowing, the profitability and overall return on equity can significantly increase. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to grow rapidly and maximize shareholder value.
2. Enhanced Profit Margins: Financial leverage can lead to improved profit margins by allowing companies to spread fixed costs over a larger asset base. This is especially true for businesses with high operating leverage, as the fixed costs remain constant while sales increase. As a result, the profit margins expand, leading to higher profitability.
3. Capitalizing on Investment Opportunities: Financial leverage enables individuals and businesses to capitalize on investment opportunities that would otherwise be out of reach without borrowing. It provides access to additional capital, allowing for the pursuit of growth initiatives, such as expanding operations, acquiring new assets, or entering new markets. By leveraging debt, companies can accelerate their growth and potentially gain a competitive advantage.
Disadvantages of Financial Leverage:
1. Increased Financial Risk: One of the primary concerns with financial leverage is the increased financial risk it introduces. Higher levels of debt mean higher interest payments and greater financial obligations. If the investments made with borrowed funds underperform, the company may struggle to meet its debt obligations, leading to financial distress and potential bankruptcy. It is crucial to assess the company’s ability to generate sufficient cash flow to service the debt before employing financial leverage.
2. Interest Rate Sensitivity: Financial leverage exposes businesses to interest rate fluctuations. If interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, putting additional pressure on cash flow and profitability. This can be particularly challenging for companies with a significant amount of variable rate debt. It is important to consider interest rate risk and have strategies in place to manage it effectively.
3. Loss of Control: Taking on debt often means taking on additional stakeholders in the form of creditors or lenders. This can result in a loss of control for business owners or shareholders, as the company may be required to adhere to certain covenants or restrictions imposed by lenders. It is important to carefully consider the terms and conditions associated with debt financing and ensure they align with the company’s long-term objectives.
In summary, financial leverage offers the potential for increased returns and enhanced profitability, enabling businesses to pursue growth opportunities that would be otherwise inaccessible. However, it comes with inherent risks, including increased financial obligations, interest rate sensitivity, and a potential loss of control. Businesses must carefully assess their risk tolerance, cash flow capabilities, and long-term goals before deciding to employ financial leverage.
By conducting thorough financial analysis, implementing risk management strategies, and maintaining a healthy balance between debt and equity, companies can effectively harness the benefits of financial leverage while mitigating its potential drawbacks.
5- Real-Life Examples of Financial Leverage in the World Context:
To provide a practical understanding of financial leverage, it’s important to examine real-life examples of companies that have effectively utilized this strategy to achieve significant growth and profitability. Here are three prominent case studies that demonstrate the successful implementation of financial leverage:
1. Case Study: Apple Inc.:
Apple Inc., one of the world’s leading technology companies, has employed financial leverage to fuel its rapid expansion and innovative product development. Apple has strategically utilized debt financing to fund its research and development initiatives, marketing campaigns, and capital expenditures. By leveraging debt, Apple has been able to finance its operations while preserving its substantial cash reserves for strategic acquisitions, stock buybacks, and other value-enhancing activities. This approach has allowed Apple to maintain a healthy debt-to-equity ratio, optimize its capital structure, and generate robust returns for its shareholders.
2. Case Study: Amazon.com Inc.:
Amazon.com Inc., the global e-commerce giant, has demonstrated the effective use of financial leverage to drive its exponential growth and diversification. Amazon has leveraged debt to fund its aggressive expansion strategies, including the acquisition of Whole Foods Market and the development of its cloud computing arm, Amazon Web Services (AWS). By leveraging debt strategically, Amazon has been able to access the capital needed to invest in infrastructure, technology advancements, and new business ventures. The company’s ability to generate consistent cash flows and demonstrate a strong growth trajectory has allowed it to effectively manage its debt obligations and create substantial value for its shareholders.
3. Case Study: The Walt Disney Company:
The Walt Disney Company, a renowned entertainment conglomerate, has leveraged debt financing to support its extensive portfolio of media networks, theme parks, and film production ventures. Disney has effectively utilized financial leverage to acquire major entertainment properties like Pixar, Marvel, and Lucasfilm, enabling it to expand its content offerings and reach a broader audience. Through prudent debt management and strategic capital allocation, Disney has maintained a solid debt-to-equity ratio and achieved consistent growth in revenue and profitability. The successful implementation of financial leverage has played a pivotal role in Disney’s global expansion and its position as a leading entertainment brand.
These case studies highlight how companies with a clear strategic vision and disciplined financial management have effectively utilized financial leverage to achieve remarkable growth and profitability. By carefully evaluating investment opportunities, optimizing capital structure, and managing debt obligations, these companies have leveraged their resources to create substantial value for their stakeholders.
By studying real-life examples like these, individuals and businesses can gain valuable insights into the practical applications of financial leverage and learn from the strategies employed by successful organizations. Understanding the specific contexts and outcomes of these case studies can provide a foundation for implementing financial leverage in your own business or investment decisions.
6- Financial Leverage in the Indian Context:
To provide a comprehensive understanding of financial leverage, it is essential to explore its application in the Indian business landscape. Here are three case studies that showcase how companies in India have leveraged debt to drive growth and establish themselves as market leaders:
1. Case Study: Tata Motors:
Tata Motors, one of India’s largest automobile manufacturers, has effectively utilized financial leverage to expand its operations and strengthen its position in the domestic and international markets. The company employed debt financing to fund its ambitious acquisition of Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) in 2008. This strategic move not only provided Tata Motors with access to premium brands and advanced technologies but also significantly expanded its global footprint. Despite the challenges faced by the automotive industry, Tata Motors has successfully managed its debt obligations and maintained a balanced debt-to-equity ratio, leveraging debt to drive growth and enhance shareholder value.
2. Case Study: Reliance Industries Limited:
Reliance Industries Limited (RIL), a diversified conglomerate with interests in energy, petrochemicals, textiles, retail, and telecommunications, has utilized financial leverage to fuel its rapid expansion and diversification. RIL has effectively employed debt financing to fund its capital-intensive projects, including the establishment of world-class refineries, petrochemical complexes, and the rollout of its telecom venture, Jio. By leveraging debt strategically, RIL has been able to fund its ambitious growth plans, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and maintain a strong market position in various sectors.
3. Case Study: Infosys Limited:
Infosys Limited, a leading Indian multinational corporation specializing in IT services and consulting, has leveraged financial resources to drive its growth and global competitiveness. Infosys has utilized debt financing to fund strategic acquisitions, research and development initiatives, and expansion into new markets. By leveraging debt strategically, Infosys has enhanced its capabilities, diversified its service offerings, and expanded its global client base. The company’s disciplined debt management and focus on generating strong cash flows have enabled it to effectively navigate the dynamic IT services landscape and deliver sustainable growth.
These case studies illustrate how companies in the Indian context have employed financial leverage to capitalize on growth opportunities, expand their operations, and create value for their stakeholders. By carefully managing debt, optimizing capital structure, and focusing on generating consistent cash flows, these companies have successfully utilized financial leverage to drive their growth strategies.
Understanding the specific approaches and outcomes of these Indian case studies provides valuable insights into the practical applications of financial leverage in the Indian business environment. It highlights the importance of strategic decision-making, risk management, and prudent debt management in leveraging debt effectively for growth and profitability.
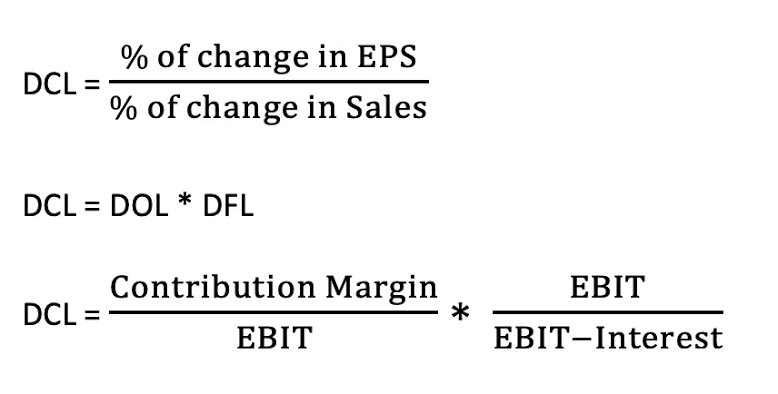
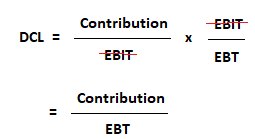
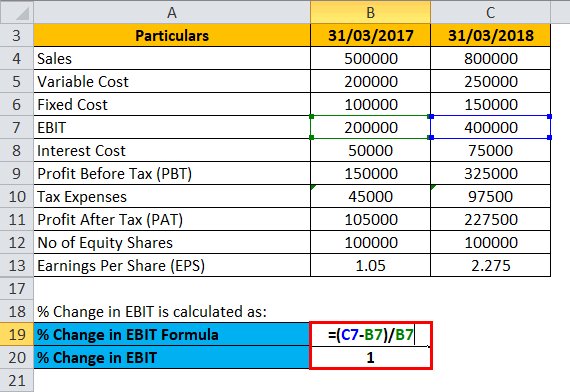
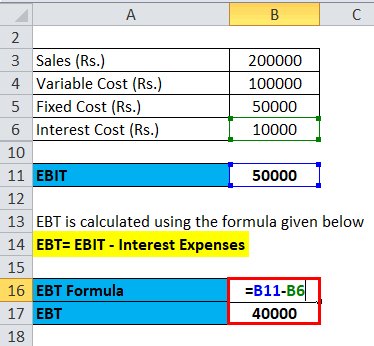
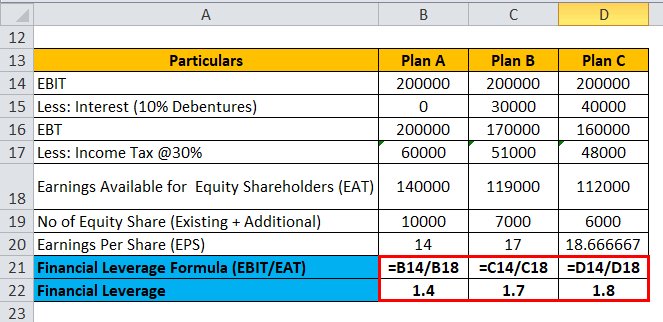
7- Numerical Analysis: Calculating Financial Leverage Ratios:
To gain a deeper understanding of financial leverage, it is important to analyze and calculate various financial leverage ratios. These ratios provide quantitative insights into a company’s leverage position and help evaluate its financial risk and solvency. Here are some key financial leverage ratios and how to calculate them:
1. Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
The debt-to-equity ratio measures the proportion of debt to equity in a company’s capital structure. It is calculated by dividing total debt by total equity.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
A high debt-to-equity ratio indicates a higher level of financial leverage, as the company relies more on borrowed funds. Conversely, a low ratio signifies a more conservative financing approach.
2. Debt Ratio:
The debt ratio measures the percentage of a company’s assets that are financed by debt. It is calculated by dividing total debt by total assets.
Debt Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets
The debt ratio provides an understanding of the company’s overall debt burden and its reliance on debt financing.
3. Interest Coverage Ratio:
The interest coverage ratio assesses a company’s ability to cover its interest payments from its operating profits. It is calculated by dividing earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by interest expenses.
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expenses
A higher interest coverage ratio indicates that the company has sufficient earnings to comfortably meet its interest obligations.
4. Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio:
The fixed charge coverage ratio measures a company’s ability to cover fixed expenses, including interest payments and lease obligations. It is calculated by dividing earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) by fixed charges.
Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio = EBITDA / (Interest Expenses + Lease Payments)
A higher fixed charge coverage ratio indicates better financial stability and the ability to meet fixed obligations.
By calculating and analyzing these financial leverage ratios, individuals and businesses can assess a company’s leverage position, risk profile, and ability to handle debt obligations. These ratios provide valuable insights into the company’s financial health and its capacity to generate sufficient cash flow to cover debt and fixed expenses.
Numerical analysis allows for a quantitative evaluation of financial leverage and helps in making informed decisions regarding capital structure, investment opportunities, and risk management strategies.
8- Applications of Financial Leverage:
Financial leverage finds applications in various scenarios, and understanding how to effectively utilize it can bring significant benefits. Here are some practical applications of financial leverage:
1. Investing in Stocks and Bonds:
Individual investors can leverage their investments by borrowing funds to invest in stocks or bonds. This approach, known as margin trading, allows investors to amplify their potential returns. By using leverage, investors can increase their purchasing power and potentially generate higher profits if the investments perform well. However, it is important to note that margin trading also amplifies the risks, and careful risk management is essential to avoid substantial losses.
2. Starting or Expanding a Business:
Entrepreneurs often employ financial leverage when starting or expanding a business. By using debt financing, entrepreneurs can access the necessary capital to fund initial investments, acquire assets, and cover operational expenses. Debt financing allows businesses to conserve their own capital and allocate it to other growth opportunities. However, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the company’s cash flow projections, profitability, and ability to service debt before taking on significant levels of leverage.
3. Mergers and Acquisitions:
Financial leverage plays a crucial role in mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activities. Acquiring companies often employ debt financing to fund the purchase of the target company. By leveraging debt, acquiring companies can minimize the need for equity financing and potentially enhance the financial returns of the transaction. However, careful due diligence, valuation analysis, and consideration of the target company’s financial health are essential to ensure that the debt burden can be managed effectively post-acquisition.
4. Capitalizing on Growth Opportunities:
Financial leverage can be utilized to capitalize on growth opportunities, such as expanding into new markets, launching new products, or acquiring complementary businesses. By employing debt financing, companies can access the necessary funds to execute their growth strategies. However, it is important to carefully assess the potential risks and rewards of each opportunity and ensure that the projected returns justify the increased debt obligations.
5. Real Estate Investments:
Real estate investors often utilize financial leverage to acquire properties. By obtaining a mortgage or other forms of debt financing, investors can increase their purchasing power and acquire properties that would otherwise be out of reach. Financial leverage in real estate investments can potentially enhance returns through rental income and property value appreciation. However, it is essential to carefully evaluate the rental income potential, market conditions, and associated risks before leveraging real estate investments.
It is important to note that while financial leverage offers opportunities for increased returns, it also introduces risks. Careful evaluation of the specific circumstances, financial analysis, risk management, and prudent decision-making are crucial when applying financial leverage in different scenarios.
9- Critical Analysis of Financial Leverage:
While financial leverage can be a powerful strategy for enhancing returns and driving growth, it is important to critically analyze its potential pitfalls and limitations. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Risk Management:
Financial leverage amplifies both gains and losses. It increases the potential for higher returns, but it also magnifies the risks associated with debt obligations. It is crucial to assess the company’s ability to generate sufficient cash flow to service the debt, especially during challenging economic conditions or industry downturns. Adequate risk management practices, including stress testing and contingency planning, are essential to mitigate the potential downsides of financial leverage.
2. Interest Rate Sensitivity:
Financial leverage exposes businesses to interest rate fluctuations. If interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, which can put pressure on cash flow and profitability. Companies should carefully consider interest rate risk and have strategies in place to manage it effectively. This may involve utilizing fixed-rate debt or implementing interest rate hedging instruments to minimize the impact of interest rate movements.
3. Industry and Business Dynamics:
The suitability of financial leverage varies across industries and business models. Some industries, such as utilities or stable cash flow businesses, can handle higher levels of debt due to their stable revenue streams. On the other hand, industries characterized by volatility or cyclical fluctuations may require a more conservative approach to debt financing. It is essential to consider the specific dynamics of the industry and the company’s business model when determining the appropriate level of financial leverage.
4. Flexibility and Liquidity:
Financial leverage can limit a company’s flexibility and liquidity. High debt levels may restrict the company’s ability to pursue new opportunities, invest in research and development, or withstand unexpected financial challenges. Maintaining a healthy balance between debt and equity is crucial to ensure adequate financial flexibility and liquidity, allowing the company to respond to changing market conditions and seize new opportunities.
5. Long-Term Sustainability:
The sustainability of financial leverage depends on the company’s ability to generate consistent cash flows and manage its debt obligations over the long term. Overreliance on debt financing without a solid revenue and cash flow generation strategy can lead to financial distress and potentially bankruptcy. It is essential to strike a balance between debt and equity, maintain a healthy debt-to-equity ratio, and focus on sustainable growth rather than short-term gains.
Critical analysis helps in understanding the potential risks and limitations associated with financial leverage. It emphasizes the importance of prudent decision-making, risk management practices, and a long-term perspective when employing financial leverage.
10- Conclusion:
Financial leverage is a powerful tool that, when used strategically, can unlock opportunities for growth and enhanced profitability. By leveraging debt, individuals and businesses can amplify their potential returns and achieve their financial objectives. However, it is important to approach financial leverage with a comprehensive understanding of its nuances and potential risks.
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the concept of financial leverage in depth, examining its various types, advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications. We have delved into real-life examples and case studies from both global and Indian contexts, showcasing how companies have effectively utilized financial leverage to drive growth and create value.
The key takeaways from our discussion include:
1. Financial leverage can increase returns on equity and profit margins, providing an avenue for accelerated growth and expansion.
2. Understanding the different types of financial leverage, such as operating leverage, financial leverage, and combined leverage, is crucial for making informed decisions and optimizing capital structure.
3. Careful risk management, including assessing the company’s ability to generate cash flow and manage debt obligations, is essential when employing financial leverage.
4. Financial leverage finds applications in various scenarios, such as investing in stocks and bonds, starting or expanding a business, engaging in mergers and acquisitions, and capitalizing on growth opportunities.
5. Critical analysis is necessary to evaluate the potential risks and limitations of financial leverage, including interest rate sensitivity, industry dynamics, flexibility, and long-term sustainability.
By considering these key points, individuals and businesses can navigate the complexities of financial leverage and make informed decisions that align with their goals and risk tolerance.
It is important to emphasize that the application of financial leverage requires careful evaluation, prudent decision-making, and ongoing monitoring. Each situation is unique, and the suitability of financial leverage may vary based on the specific circumstances.
As you continue your journey in understanding and utilizing financial leverage, always remember the importance of maintaining a balance between risk and reward. Regularly assess your financial position, adapt to changing market conditions, and make well-informed choices to optimize growth, profitability, and long-term sustainability.
With a comprehensive understanding of financial leverage and its practical implications, you are well-equipped to make informed decisions and leverage debt as a catalyst for growth and profitability.
Leave a comment