

## Index
1. Introduction to Capital Budgeting
2. Importance of Capital Budgeting in Business Decisions
3. Understanding Investment Appraisal Techniques
a. Payback Period
b. Net Present Value (NPV)
c. Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
d. Profitability Index (PI)
e. Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
4. Real-Life Examples of Successful Capital Budgeting in the World Context
a. Tech Giant’s Expansion Strategy
b. Sustainable Energy Investment Project
c. Infrastructure Development for a Developing Nation
5. Indian Context: Capital Budgeting in a Diverse Economy
a. Manufacturing Sector Modernization
b. Healthcare Industry’s Growth Plans
c. Renewable Energy Ventures
6. Case Studies on Capital Budgeting
a. Automobile Company’s Product Line Expansion
b. Retail Chain’s Store Expansion Decision
c. IT Services Company’s Merger and Acquisition Strategy
7. The Role of Numericals in Capital Budgeting Analysis
a. Quantitative Decision-Making Process
b. Calculating Cash Flows
c. Sensitivity Analysis and Risk Assessment
8. Practical Applications of Capital Budgeting Techniques
a. Capital Rationing and Resource Allocation
b. Replacement and Retirement Decisions
c. Mutually Exclusive Projects Evaluation
9. Critical Analysis of Capital Budgeting Methods
a. Advantages and Limitations of NPV
b. Assessing IRR’s Flaws
c. The Value of PI in Investment Decisions
10. Capital Budgeting in a Volatile Economic Environment
a. Inflation’s Impact on Decision Making
b. Economic Uncertainty and Long-Term Investments
11. Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Capital Budgeting
Hello there, valued readers!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Capital Budgeting – a vital aspect of making informed investment decisions in the corporate world. In this blog post, we’ll take you on an enlightening journey through the nature of investment, its importance, and practical applications with real-life examples from around the globe and the Indian context. So let’s get started!
Chapter 1: Introduction to Capital Budgeting
Hello, dear readers! In this chapter, we’ll embark on an exciting journey to explore the fundamentals of capital budgeting and its significance in the world of investments. So, let’s dive in!
### What is Capital Budgeting?
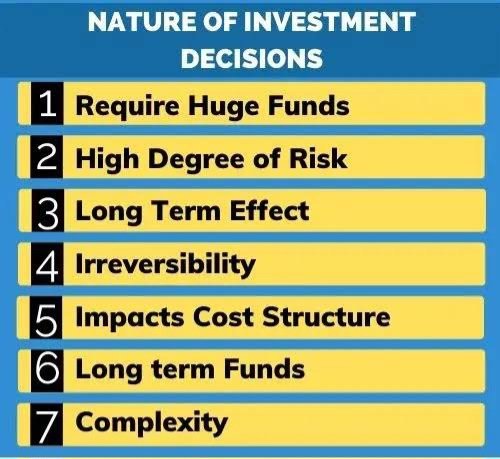
Capital budgeting is a strategic process used by businesses to evaluate potential investment projects or opportunities. These investments typically involve substantial amounts of money and are long-term in nature, with the aim of generating returns over an extended period. The goal of capital budgeting is to determine whether an investment is worth pursuing and aligns with the company’s overall financial objectives.
### The Nature of Investment
Investment decisions often have far-reaching consequences for a company’s success and growth trajectory. Companies may consider various types of investments, such as:
1. **Expansion Projects**: Investing in expanding existing facilities or opening new branches or subsidiaries.
2. **Replacement Projects**: Replacing outdated equipment or machinery to improve operational efficiency and productivity.
3. **Research and Development**: Funding new product development or innovative technologies to gain a competitive edge.
4. **Acquisitions and Mergers**: Buying or merging with other companies to enhance market share or diversify operations.
5. **Infrastructure Development**: Investing in infrastructure projects to support business operations and growth.
### The Importance of Capital Budgeting
Now, you might be wondering why capital budgeting is so crucial for businesses. Well, here are some compelling reasons:
1. **Resource Allocation**: Companies have limited financial resources, and capital budgeting helps them prioritize projects that promise the highest return on investment.
2. **Risk Management**: By analyzing potential risks and returns, capital budgeting allows companies to make informed decisions and reduce uncertainties.
3. **Long-Term Planning**: Capital budgeting is essential for aligning investments with long-term corporate strategies, ensuring sustainable growth.
4. **Maximizing Shareholder Value**: Sound investment decisions lead to increased profitability, which benefits shareholders and stakeholders alike.
5. **Competitive Advantage**: Making the right investments can give companies a competitive advantage in their industry.
### Investment Appraisal Techniques
In capital budgeting, various techniques aid in evaluating the feasibility of investment projects. Let’s briefly explore some popular ones:
1. **Payback Period**: This technique calculates the time required for an investment to recoup its initial cost. Companies often prefer shorter payback periods as they signify quicker returns.
2. **Net Present Value (NPV)**: NPV assesses the profitability of an investment by comparing the present value of expected cash inflows to the initial investment. A positive NPV indicates a financially viable project.
3. **Internal Rate of Return (IRR)**: IRR is the discount rate at which the NPV of an investment becomes zero. It measures the project’s potential rate of return and helps compare it to other investment opportunities.
4. **Profitability Index (PI)**: Also known as the Benefit-Cost Ratio, PI measures the ratio of present value of cash inflows to the initial investment. A PI greater than 1 indicates a profitable venture.
5. **Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)**: ARR is calculated by dividing the average annual accounting profit by the initial investment. While straightforward, ARR does not consider the time value of money.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve explored the foundation of capital budgeting and its significance in making prudent investment decisions. As we progress through this blog post, we’ll delve deeper into specific investment appraisal techniques, real-life examples, and practical applications from around the world and India. Stay tuned for more insightful chapters ahead!
Chapter 2: Importance of Capital Budgeting in Business Decisions
Welcome back, readers! In this chapter, we will delve deeper into why capital budgeting holds immense importance in shaping the destiny of businesses and their long-term success. Let’s explore the significance of this critical process:
### Efficient Resource Allocation
One of the primary reasons capital budgeting is crucial for businesses is its role in resource allocation. Companies often have limited funds, and choosing the right investment projects can significantly impact their financial health. Capital budgeting helps allocate resources to projects that offer the highest potential for returns, ensuring optimal use of available funds.
### Risk Management and Decision Making
Investment decisions are inherently associated with risks. Capital budgeting enables companies to identify, assess, and mitigate these risks through thorough analysis. By considering factors such as market conditions, technological advancements, and potential competitors, businesses can make informed decisions that reduce uncertainties and maximize returns.
### Long-Term Planning and Sustainable Growth
Businesses cannot thrive without a well-defined long-term strategy. Capital budgeting aligns investment decisions with the company’s broader goals and objectives, fostering sustainable growth. Whether it’s expanding market presence, enhancing production capabilities, or adopting eco-friendly practices, capital budgeting ensures that investments contribute to the company’s future success.
### Maximizing Shareholder Value
Shareholders play a crucial role in any company’s growth. Capital budgeting allows businesses to identify projects that generate higher returns, thereby increasing shareholder value. When shareholders see profitable ventures, they are more likely to invest further and have confidence in the company’s management.
### Competing in the Market
The business landscape is highly competitive, and capital budgeting can give companies a competitive edge. By making smart investments, businesses can offer better products, improve customer experiences, and stay ahead of their rivals.
### Enhancing Capital Efficiency
Capital budgeting helps identify projects that have the potential to generate higher returns with lower capital requirements. This efficiency ensures that companies do not tie up excessive funds in projects that do not yield substantial benefits.
### Adapting to Dynamic Business Environment
Market conditions are ever-changing, and businesses must adapt to survive. Capital budgeting enables companies to be agile and responsive to economic fluctuations, technological advancements, and changes in consumer preferences.
### Balancing Short-term and Long-term Goals
Often, companies face a dilemma between short-term profitability and long-term sustainability. Capital budgeting assists in striking the right balance, ensuring that investment decisions align with both immediate financial objectives and the company’s overall growth strategy.
### Engaging Stakeholders
Investment decisions can significantly impact various stakeholders, such as employees, suppliers, and the local community. Capital budgeting facilitates transparent communication with stakeholders, as companies can demonstrate how their investments positively impact everyone involved.
### Responsible Corporate Citizenship
Incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions is becoming increasingly important for businesses. Capital budgeting allows companies to evaluate projects from an ESG perspective, demonstrating a commitment to responsible corporate citizenship.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we have explored the critical role capital budgeting plays in shaping business decisions and the long-term success of companies. By efficiently allocating resources, mitigating risks, fostering sustainable growth, and maximizing shareholder value, capital budgeting becomes an indispensable tool for any organization seeking prosperity in a dynamic and competitive world.
Chapter 3: Understanding Investment Appraisal Techniques
Hello again, dear readers! In this chapter, we’ll dive into the world of investment appraisal techniques – the analytical tools that guide businesses in evaluating the feasibility and profitability of potential projects. Let’s explore each method and its applications:
### 1. Payback Period
The payback period is a simple and intuitive method to assess how quickly an investment will recover its initial cost. It calculates the time required for the cumulative cash inflows to equal the initial investment. Businesses often use the payback period to evaluate the liquidity of an investment and prefer shorter payback periods as they signify quicker returns.
**Application**: The payback period is useful when companies have limited capital and need to recover their investments swiftly. It is commonly employed for projects with relatively short-term benefits, such as technology upgrades or equipment replacements.
### 2. Net Present Value (NPV)
NPV is a powerful technique used to determine the profitability of an investment by comparing the present value of expected cash inflows to the initial investment. A positive NPV indicates that the investment is expected to generate returns above the required rate of return.
**Application**: NPV is widely used in capital budgeting due to its ability to account for the time value of money and provide a clear indicator of an investment’s value. Businesses can use NPV to rank and prioritize projects based on their profitability.
### 3. Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
IRR is the discount rate at which the NPV of an investment becomes zero, meaning that the project’s benefits equal its costs. It measures the potential rate of return an investment offers and is often used as a decision-making tool to compare projects.
**Application**: Companies use IRR to assess whether the expected return from an investment exceeds the cost of capital. If the IRR is higher than the cost of capital, the project is considered financially viable.
### 4. Profitability Index (PI)
Also known as the Benefit-Cost Ratio, the Profitability Index calculates the ratio of the present value of cash inflows to the initial investment. A PI greater than 1 indicates that the investment is expected to generate positive returns.
**Application**: The PI complements other investment appraisal techniques by providing an additional metric to rank projects based on their profitability. It helps companies evaluate the efficiency of resource allocation among different projects.
### 5. Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
ARR evaluates an investment’s profitability by dividing the average annual accounting profit by the initial investment cost. Though straightforward, ARR does not consider the time value of money, making it less robust compared to NPV and IRR.
**Application**: ARR is primarily used as a supplemental technique in situations where companies require a quick and straightforward assessment of investment profitability.
### Choosing the Right Technique
Selecting the most appropriate appraisal technique depends on the specific characteristics and requirements of each investment project. Companies often use multiple techniques together to gain a comprehensive understanding of their investment decisions.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve explored the various investment appraisal techniques available to businesses. Each method offers unique insights into investment feasibility and profitability. By employing these techniques, companies can make informed and data-driven decisions, ensuring that their investments align with their strategic goals and lead to long-term success.
Chapter 4: Real-Life Examples of Successful Capital Budgeting in the World Context
Welcome back, avid readers! In this chapter, we’ll explore real-life examples of successful capital budgeting initiatives from around the world. These examples will illustrate how strategic investment decisions have propelled companies to greater heights. Let’s dive in and draw inspiration from these success stories:
### 1. Tech Giant’s Expansion Strategy
A global technology company with a dominant presence in the software industry recognized the potential of the cloud computing market. Despite the substantial capital required for infrastructure and research, the company undertook a bold capital budgeting decision to expand its cloud services division. Through thorough market analysis and risk assessment, the company projected high demand for cloud services in the coming years.
Their foresight and strategic investment paid off handsomely, as the cloud services division experienced exponential growth. The company’s early entry into the market allowed them to establish a strong foothold and secure long-term contracts with major clients. Today, the cloud division contributes significantly to the company’s overall revenue, making it a prime example of successful capital budgeting.
### 2. Sustainable Energy Investment Project
A forward-thinking utility company recognized the need for a transition to sustainable energy sources amidst growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. They allocated a substantial portion of their capital budget to invest in renewable energy projects such as solar farms and wind turbines.
While the initial costs were higher compared to conventional energy projects, the long-term benefits were undeniable. The investment not only contributed to environmental conservation but also enabled the company to diversify its energy portfolio and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. In a short time, the sustainable energy division became a profitable segment, attracting environmentally-conscious consumers and investors.
### 3. Infrastructure Development for a Developing Nation
A multinational construction and engineering company saw great potential in investing in infrastructure projects in a developing nation. Recognizing the nation’s efforts to modernize its transportation and utilities systems, the company allocated a significant portion of its capital budget to undertake large-scale projects, including building roads, bridges, and power plants.
The company’s strategic decision to enter this market at the right time allowed them to secure lucrative contracts and government partnerships. As the nation’s infrastructure improved, the demand for their services surged, resulting in significant profits and a reputation as a reliable partner for future projects.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve explored real-life examples of how successful capital budgeting has propelled companies to achieve remarkable success. These case studies highlight the importance of foresight, analysis, and risk assessment in making sound investment decisions. Whether it’s expanding into new markets, embracing sustainable practices, or participating in nation-building efforts, capital budgeting has played a key role in shaping these success stories.
Chapter 5: Indian Context: Capital Budgeting in a Diverse Economy
Namaste, dear readers! In this chapter, we’ll shift our focus to the Indian context and explore how capital budgeting has driven growth and innovation in diverse industries within the country. India’s dynamic economy offers a myriad of opportunities for strategic investment decisions. Let’s delve into some examples:
### 1. Manufacturing Sector Modernization
In India’s ever-evolving manufacturing landscape, capital budgeting has been instrumental in enabling companies to embrace modern technologies and stay competitive in the global market. An Indian automobile manufacturer, for instance, recognized the need to upgrade its production facilities and invest in automation to boost efficiency and reduce costs.
Through careful analysis and financial planning, the company allocated a substantial capital budget to implement state-of-the-art manufacturing processes and advanced robotics. The investment led to streamlined operations, improved product quality, and increased production capacity. As a result, the company witnessed significant growth in market share and profitability, solidifying its position as a leading player in the industry.
### 2. Healthcare Industry’s Growth Plans
The healthcare sector in India has seen tremendous growth, driven by increased demand for quality healthcare services. A prominent hospital chain capitalized on this opportunity by strategically allocating its capital budget to expand its network of medical facilities across the country.
Through meticulous market research and demand analysis, the hospital chain identified underserved regions with a growing population. By investing in new hospitals and healthcare centers, the company brought quality healthcare services closer to the people. The strategic expansion not only improved access to medical care but also boosted the company’s revenues and brand reputation.
### 3. Renewable Energy Ventures
India, as a developing nation, faces both the challenge of meeting its growing energy demands and the responsibility of sustainable development. Several companies have successfully ventured into renewable energy projects through strategic capital budgeting.
A renewable energy developer identified the potential for solar energy in specific regions and allocated a significant portion of its capital budget to build solar power plants. The investment not only contributed to reducing the nation’s carbon footprint but also brought in a steady stream of revenue through long-term power purchase agreements. This forward-looking approach earned the company recognition as a leading player in the clean energy sector.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve explored how capital budgeting has driven growth and innovation in the Indian economy across various industries. Through strategic investment decisions, companies have modernized manufacturing, expanded healthcare services, and embraced renewable energy, contributing to the nation’s progress.
Capital budgeting plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of businesses in India, allowing them to leverage opportunities, mitigate risks, and achieve sustainable growth. In the following chapters, we’ll delve deeper into more case studies, practical applications, and critical analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of this vital financial process.
Chapter 6: Case Studies on Capital Budgeting
Hello once again, curious readers! In this chapter, we’ll dive into case studies that demonstrate how capital budgeting has influenced actual investment decisions in different scenarios. These real-life examples will provide valuable insights into the complexities of capital budgeting and its impact on businesses. Let’s explore:
### 1. Automobile Company’s Product Line Expansion
An established automobile company faced a critical decision when considering expanding its product line to include electric vehicles (EVs). The management understood the potential of EVs in the market, but they also acknowledged the high upfront costs and uncertain demand for electric vehicles at that time.
Through a rigorous capital budgeting process, the company analyzed projected sales, manufacturing costs, government incentives, and potential competitors. The analysis revealed that the demand for EVs was likely to grow rapidly in the coming years, and the long-term benefits outweighed the initial investment.
The company decided to allocate a significant portion of its capital budget to research and development for EV technology and building a state-of-the-art production facility. Their strategic move paid off as they launched a successful line of electric vehicles, gaining a competitive edge in the growing EV market.
### 2. Retail Chain’s Store Expansion Decision
A retail chain, with a well-established presence in urban areas, wanted to expand its operations to rural regions. However, they were uncertain about the profitability of new stores in these untapped markets.
Through a comprehensive capital budgeting analysis, the retail chain assessed various factors, such as population demographics, purchasing power, and logistical challenges. The analysis revealed that while the initial costs of setting up stores in rural areas were high, the potential market size and reduced competition presented a promising opportunity.
The retail chain decided to allocate a portion of its capital budget to open stores in select rural locations. The well-planned expansion allowed the company to tap into new customer segments and gain a first-mover advantage. As a result, the company experienced significant revenue growth and strengthened its position as a leading retail player.
### 3. IT Services Company’s Merger and Acquisition Strategy
An IT services company recognized the need to expand its service offerings and geographical reach to meet the growing demands of its clients. The management explored several options, including organic growth and strategic partnerships, but ultimately decided to pursue a merger and acquisition (M&A) strategy.
Through a thorough capital budgeting evaluation, the company assessed potential M&A targets, integration costs, expected synergies, and potential risks. The analysis highlighted a target company that complemented their existing services and had a strong customer base.
The company allocated a substantial capital budget to acquire the target company and integrate their operations seamlessly. The M&A proved successful as it expanded the company’s service portfolio, improved market share, and delivered cost efficiencies through synergies.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve explored case studies that demonstrate how capital budgeting plays a crucial role in shaping investment decisions. Whether it’s expanding product lines, opening new stores, or pursuing strategic mergers, capital budgeting allows companies to make informed choices that lead to growth and success.
These case studies illustrate the importance of conducting thorough analyses, considering various scenarios, and being forward-thinking when allocating capital budgets. In the following chapters, we’ll delve into the role of numericals and practical applications in capital budgeting, providing you with a deeper understanding of this essential financial process.
Chapter 7: The Role of Numericals in Capital Budgeting Analysis
Welcome back, inquisitive readers! In this chapter, we’ll explore the critical role of numerical analysis in capital budgeting. Numbers and data play a pivotal role in making informed investment decisions. Let’s delve into how numericals aid in the evaluation of potential projects:
### 1. Quantitative Decision-Making Process
Capital budgeting involves a quantitative approach to assess the financial viability of investment opportunities. Numerical analysis allows businesses to compare different projects based on their projected cash flows, profitability, and risk factors. This data-driven decision-making process ensures that investments align with the company’s financial objectives.
### 2. Calculating Cash Flows
Forecasting cash flows is at the heart of capital budgeting. Businesses must estimate the expected inflows and outflows of cash associated with an investment project over its entire life cycle. Accurate cash flow projections help determine the project’s net benefits and whether it will generate positive returns.
### 3. Sensitivity Analysis and Risk Assessment
Numericals enable companies to conduct sensitivity analysis, evaluating how changes in key variables impact investment outcomes. This process helps identify the most critical factors affecting the project’s profitability and risk. By considering different scenarios, companies can make robust and risk-aware decisions.
### 4. Cost of Capital and Discount Rate Calculation
The cost of capital or discount rate is a crucial parameter in many capital budgeting techniques, such as NPV and IRR. Numericals allow businesses to determine an appropriate discount rate, reflecting the opportunity cost of capital and the project’s inherent risk.
### 5. Incorporating Inflation and Time Value of Money
Numericals facilitate adjusting cash flows for inflation and incorporating the time value of money. As cash flows received in the future are worth less than those received today, businesses must apply appropriate discounting and inflation factors to make accurate investment evaluations.
### 6. Measuring Return on Investment (ROI)
Numerical analysis enables companies to measure the return on investment for a project accurately. ROI is a critical metric to assess how efficiently a project generates profits relative to its cost. This metric aids in comparing investment opportunities and choosing the most promising ones.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve explored the indispensable role of numerical analysis in capital budgeting. From calculating cash flows and assessing risk to determining discount rates and measuring ROI, numericals provide the necessary foundation for making informed and data-driven investment decisions.
Numerical analysis helps businesses mitigate uncertainties, identify opportunities, and allocate resources wisely. In the subsequent chapters, we’ll delve into practical applications of capital budgeting techniques, critical analysis of their advantages and limitations, and how companies navigate volatile economic environments to achieve their financial goals.
Chapter 8: Practical Applications of Capital Budgeting Techniques
Welcome back, insightful readers! In this chapter, we’ll explore the practical applications of capital budgeting techniques in real-world scenarios. These techniques serve as invaluable tools for businesses to make well-informed investment decisions. Let’s delve into some of their practical applications:
### 1. Capital Rationing and Resource Allocation
In situations where companies have limited funds, capital budgeting techniques aid in prioritizing investment projects. By comparing the expected returns and profitability of different projects, businesses can allocate resources to those projects that offer the highest value for money. This approach ensures efficient resource utilization and maximizes overall returns.
### 2. Replacement and Retirement Decisions
Capital budgeting techniques also play a crucial role when companies need to decide whether to replace or retire existing assets. By comparing the expected cash flows of a new asset with the ongoing costs of maintaining the old one, businesses can assess the financial viability of replacing outdated equipment or machinery.
### 3. Mutually Exclusive Projects Evaluation
Sometimes, companies may have multiple investment opportunities that serve the same purpose or target similar markets. Capital budgeting techniques help in evaluating mutually exclusive projects and selecting the one that offers the best financial outcomes. This analysis considers factors such as profitability, risk, and strategic alignment.
### 4. Strategic Investment Planning
Strategic investment planning involves aligning investment decisions with the long-term goals and objectives of the company. Capital budgeting techniques assist businesses in evaluating potential projects that contribute to the organization’s growth and competitiveness. This approach ensures that investments are in line with the company’s overall strategy.
### 5. Measuring Environmental and Social Impact
As environmental and social considerations gain importance, companies are using capital budgeting techniques to assess the impact of investment projects. By incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into their analysis, businesses can make responsible investment decisions that align with sustainability goals.
### 6. Evaluating Research and Development (R&D) Projects
Innovation is crucial for a company’s long-term success. Capital budgeting techniques are applied to assess the potential returns from research and development (R&D) projects. By quantifying the expected benefits and risks of innovation initiatives, companies can prioritize R&D investments that offer the best chances of success.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve explored the practical applications of capital budgeting techniques that businesses use to make informed investment decisions. From resource allocation and replacement decisions to strategic investment planning and ESG considerations, these techniques empower companies to navigate complex financial choices.
Capital budgeting ensures that investments are aligned with financial objectives, risk tolerance, and long-term growth strategies. In the following chapters, we’ll critically analyze the advantages and limitations of specific capital budgeting methods, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of their real-world implications.
Chapter 9: Critical Analysis of Capital Budgeting Methods
Welcome back, thoughtful readers! In this chapter, we’ll critically analyze some of the key capital budgeting methods, exploring their advantages and limitations. While these techniques are valuable tools for investment appraisal, it’s essential to understand their real-world implications. Let’s delve into the critical analysis:
### 1. Advantages and Limitations of Net Present Value (NPV)
Advantages:
– NPV considers the time value of money, providing a more accurate representation of an investment’s profitability.
– It accounts for all cash flows over the project’s life, enabling a comprehensive analysis of the investment.
– NPV is particularly useful for comparing projects with different durations and investment sizes.
Limitations:
– NPV assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the discount rate, which might not always be practical.
– The method can be sensitive to changes in the discount rate and future cash flow projections, leading to potential uncertainties.
### 2. Assessing the Flaws of Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Advantages:
– IRR considers the time value of money and provides a single percentage figure for decision-making.
– It is a useful metric for comparing projects and determining the minimum rate of return needed for the investment to be viable.
Limitations:
– IRR can result in multiple or no solutions in complex cash flow patterns, leading to difficulties in interpreting results.
– The method assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR, which might not be realistic in practice.
### 3. The Value of Profitability Index (PI) in Investment Decisions
Advantages:
– PI provides a straightforward measure of an investment’s profitability relative to its cost.
– It allows companies to prioritize projects based on their profitability per unit of investment.
Limitations:
– PI does not account for the time value of money, leading to potential inaccuracies in comparing long-term projects.
– The method may favor smaller projects with higher PI values, neglecting larger but more strategic ventures.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve critically analyzed some of the key capital budgeting methods, understanding their advantages and limitations. Each technique offers valuable insights into investment decisions, but they should be used judiciously and in conjunction with other tools.
Successful capital budgeting requires a comprehensive understanding of each method’s implications, as well as an awareness of the underlying assumptions and potential risks. By applying these techniques thoughtfully, businesses can make well-informed investment choices and drive their long-term growth and success.
In the following chapters, we’ll explore the challenges and opportunities of capital budgeting in a volatile economic environment, where businesses must adapt and innovate to thrive.
Chapter 10: Capital Budgeting in a Volatile Economic Environment
Hello again, adaptable readers! In this final chapter, we’ll explore the challenges and opportunities of capital budgeting in a volatile economic environment. Economic fluctuations, uncertainties, and changing market conditions pose unique challenges for businesses. Let’s delve into how companies can navigate such an environment to make successful investment decisions:
### 1. Inflation’s Impact on Decision Making
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, making it essential for businesses to account for its effects in capital budgeting. When estimating cash flows and discount rates, companies must consider inflation rates to ensure accurate projections. Failure to do so could lead to unrealistic expectations and potentially undermine the viability of investment projects.
### 2. Economic Uncertainty and Long-Term Investments
In a volatile economic environment, businesses may hesitate to commit to long-term investments due to uncertain future cash flows. However, certain projects, such as infrastructure development or R&D initiatives, require long-term planning. Companies can mitigate this uncertainty by incorporating sensitivity analysis into their capital budgeting process, allowing them to assess potential outcomes under different economic scenarios.
### 3. Capital Rationing and Strategic Prioritization
During economic downturns or financial constraints, companies may face capital rationing, where they have limited funds to allocate to various projects. In such situations, it becomes crucial to prioritize projects strategically. Capital budgeting techniques, such as NPV and IRR, can help companies select projects with the highest potential for returns, even in a resource-constrained environment.
### 4. Embracing Innovation and Agility
Volatility can present unexpected opportunities and challenges. Companies must be agile and responsive to market changes and technological advancements. By incorporating flexible and adaptive investment strategies, businesses can seize emerging opportunities while mitigating risks.
### 5. Scenario Planning and Risk Management
Capital budgeting in a volatile economic environment requires a robust risk management approach. Scenario planning allows companies to analyze various possible economic scenarios and their impact on investment outcomes. By identifying potential risks and their likelihood, businesses can develop contingency plans to address uncertainties effectively.
### Conclusion
In this chapter, we’ve explored how capital budgeting in a volatile economic environment demands adaptability, innovation, and prudent risk management. Economic fluctuations and uncertainties require businesses to incorporate sophisticated analysis, scenario planning, and sensitivity analysis into their investment decisions.
Successful capital budgeting in such an environment requires companies to embrace change, leverage opportunities, and maintain a long-term perspective. By making informed investment decisions that align with strategic goals and respond to market dynamics, businesses can thrive even in the face of economic volatility.
As we conclude our journey through the world of capital budgeting, we hope that this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights and understanding of this critical financial process.
Chapter 11: Conclusion – Empowering Future Investment Decisions
Congratulations, esteemed readers, on completing this comprehensive journey through the world of capital budgeting! In this final chapter, we’ll recap the key takeaways and reflect on the significance of capital budgeting in empowering future investment decisions.
### The Essence of Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting is the financial process that enables businesses to evaluate potential investment opportunities, ensuring that scarce resources are allocated to projects with the highest potential for returns. By employing various techniques like NPV, IRR, and PI, companies can make informed decisions that align with their financial objectives and long-term strategies.
### Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Throughout this blog post, we’ve explored numerous real-life examples and case studies from different industries and countries. These examples have showcased how capital budgeting has driven growth, innovation, and success for various companies. From tech giants embracing cloud services to healthcare chains expanding their reach, these success stories illustrate the power of strategic investment decisions.
### Numerical Analysis and Practical Applications
Numerical analysis lies at the core of capital budgeting, helping companies calculate cash flows, assess risk, and determine discount rates. The practical applications of capital budgeting techniques, such as resource allocation, replacement decisions, and evaluating R&D projects, empower businesses to make sound financial choices.
### Advantages and Limitations
Understanding the advantages and limitations of capital budgeting methods is crucial. While NPV, IRR, and PI provide valuable insights, they must be used thoughtfully, considering their underlying assumptions and potential risks. Critical analysis helps businesses make informed choices and navigate complexities in investment appraisal.
### Navigating a Volatile Economic Environment
In a volatile economic environment, capital budgeting becomes even more critical. Companies must adapt, embrace innovation, and manage risks to succeed. By incorporating scenario planning and agile strategies, businesses can leverage opportunities and make prudent investment decisions.
### Empowering Future Investment Decisions
As we conclude this blog post, we hope that it has equipped you with a deeper understanding of capital budgeting. Whether you are a business leader, investor, or financial professional, the knowledge gained here can empower you to make better investment decisions.
Capital budgeting is not just a financial process; it is a strategic tool that shapes the future of businesses and their long-term success. Embrace the power of data-driven decisions, innovation, and responsible investments to create a brighter and more prosperous tomorrow.
Thank you for joining us on this enriching journey. May your future investment decisions be well-informed and rewarding!
Leave a comment