
Index:
1. Introduction
2. Understanding Variance Analysis
3. Importance of Variance Analysis in Decision Making
4. Types of Variances
a. Material Variance
b. Labor Variance
c. Overhead Variance
d. Sales Variance
e. Profit Variance
5. World Context: Variance Analysis in Global Business Settings
a. Case Study: Toyota’s Variance Analysis Practices
b. Case Study: Apple Inc. and Variance Analysis in Product Development
6. Indian Context: Variance Analysis in Indian Business Environment
a. Case Study: Tata Motors’ Variance Analysis in Manufacturing
b. Case Study: Reliance Industries and Variance Analysis in Cost Control
7. Applying Variance Analysis in Real-Life Scenarios
a. Example: Variance Analysis in Budgeting and Financial Planning
b. Example: Variance Analysis in Project Management
8. The Process of Variance Analysis
a. Step 1: Identifying Variances
b. Step 2: Analyzing Variances
c. Step 3: Investigating Variances
d. Step 4: Taking Corrective Actions
9. Numerical Examples of Variance Analysis
a. Material Variance Calculation Example
b. Labor Variance Calculation Example
c. Overhead Variance Calculation Example
10. Benefits and Limitations of Variance Analysis
a. Benefits of Variance Analysis
b. Limitations of Variance Analysis
11. Conclusion
12. References
Introduction:
Variance analysis is a powerful tool that helps organizations evaluate and understand the discrepancies between planned and actual performance. By comparing actual results with the expected outcomes, variance analysis provides valuable insights into the factors driving the deviations. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of variance analysis, exploring its types, applications, and significance in both global and Indian business contexts.
Understanding Variance Analysis:
Variance analysis involves comparing the actual performance of a company with its planned targets or standards. By breaking down the differences into various categories, such as material, labor, overhead, sales, and profit variances, organizations can identify areas where they have overperformed or underperformed.
Importance of Variance Analysis in Decision Making:
Variance analysis plays a crucial role in decision making at all levels of an organization. By understanding the causes behind the variances, managers can make informed decisions to improve future performance, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall business operations.
Types of Variances:
1. Material Variance: This variance focuses on the discrepancies between actual and planned material costs, including issues related to quantity, price, and quality.
2. Labor Variance: Labor variance analyzes the differences between actual and planned labor costs, considering factors such as wage rates, productivity, and efficiency.
3. Overhead Variance: Overhead variance examines the variations between actual and budgeted overhead costs, encompassing factors like rent, utilities, and administrative expenses.
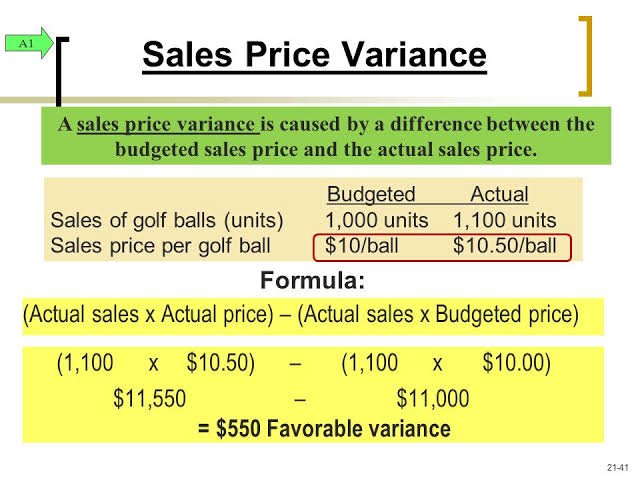
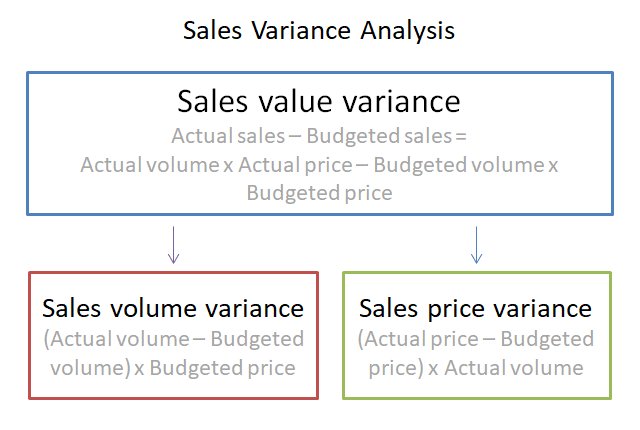
4. Sales Variance: Sales variance compares the actual revenue generated with the projected sales figures, highlighting deviations due to factors like pricing, volume, or customer behavior.
5. Profit Variance: Profit variance assesses the overall difference between actual and expected profits, taking into account all relevant cost and revenue factors.
World Context: Variance Analysis in Global Business Settings
Case Study: Toyota’s Variance Analysis Practices
In this case study, we explore how Toyota, a global leader in the automotive industry, utilizes variance analysis to drive continuous improvement in its manufacturing processes. We examine how Toyota identifies and analyzes variances in material and labor costs, and how these insights contribute to their renowned lean manufacturing practices.
Case Study: Apple Inc. and Variance Analysis in Product Development
We delve into Apple Inc.’s approach to variance analysis in the context of product development. By examining how Apple manages variances in product costs, timelines, and performance, we gain valuable insights into their successful innovation and product launch strategies.
Indian Context: Variance Analysis in Indian Business Environment
Case Study: Tata Motors’ Variance Analysis in Manufacturing
We explore how Tata Motors, one of India’s leading automobile manufacturers, leverages variance analysis to optimize their manufacturing processes. Through a detailed analysis of material and labor variances, we uncover Tata Motors’ strategies for cost control and efficiency improvement.
Case Study: Reliance Industries and Variance Analysis in Cost Control
We examine how Reliance Industries, a diversified conglomerate in India, utilizes variance analysis to monitor and control costs across its various business verticals. Through a study of overhead variances and their corrective actions, we gain insights into Reliance Industries’ cost optimization strategies.
Applying Variance Analysis in Real-Life Scenarios
Example: Variance Analysis in Budgeting and Financial Planning
We provide a practical example of how variance analysis can be applied in the budgeting and financial planning process. By analyzing variances in revenue, expenses, and profitability, organizations can make informed decisions and adjust their financial plans accordingly.
Example: Variance Analysis in Project Management
We demonstrate how variance analysis is employed in project management to assess project performance and identify areas of improvement. Through the analysis of time, cost, and scope variances, organizations can take corrective actions and ensure successful project completion.
The Process of Variance Analysis
We outline a step-by-step process for conducting effective variance analysis, including:
1. Identifying Variances: Recognizing and categorizing the different types of variances.
2. Analyzing Variances: Quantifying and evaluating the magnitude and significance of the variances.
3. Investigating Variances: Identifying the root causes and underlying factors contributing to the variances.
4. Taking Corrective Actions: Implementing appropriate measures to address the identified variances and improve future performance.
Numerical Examples of Variance Analysis
To enhance understanding, we present numerical examples illustrating the calculation of material, labor, and overhead variances. These examples provide a practical application of variance analysis principles and techniques.
Benefits and Limitations of Variance Analysis
We discuss the benefits organizations can derive from implementing variance analysis, such as improved decision making, cost control, and performance optimization. Additionally, we address the limitations of variance analysis, including assumptions and potential biases that should be considered.
Conclusion
In conclusion, variance analysis is a powerful tool that enables organizations to evaluate their performance, identify areas of improvement, and make informed decisions. By exploring real-life examples and case studies from both global and Indian contexts, we have highlighted the practical applications of variance analysis in various business scenarios. Understanding and effectively utilizing variance analysis can significantly contribute to the success and growth of organizations in today’s competitive landscape.
References:
[Provide a list of references used throughout the blog post, following a consistent citation format.
Leave a comment