

Index:
1. Introduction
2. Importance of Financial Management
3. Key Concepts in Financial Management
3.1. Time Value of Money
3.2. Risk and Return
3.3. Cost of Capital
3.4. Capital Budgeting
3.5. Financial Planning and Forecasting
3.6. Working Capital Management
3.7. Capital Structure
3.8. Dividend Policy
4. Financial Management in the World Context
4.1. Real-Life Examples: Amazon and Apple
4.2. Case Study: Tesla’s Financial Management Strategies
4.3. Application of Financial Management in International Investments
5. Financial Management in the Indian Context
5.1. Real-Life Examples: Tata Group and Reliance Industries
5.2. Case Study: Flipkart’s Financial Management Journey
5.3. Application of Financial Management in Indian Startups
6. Numerical Analysis and Calculations
6.1. Calculating Net Present Value (NPV)
6.2. Assessing Return on Investment (ROI)
6.3. Evaluating Working Capital Ratios
6.4. Analyzing Financial Statements
7. The Role of Financial Management in Decision Making
8. Conclusion
9. References
10. Categories: Finance, Management, Financial Planning
Financial Management: Concepts and Functions for Effective Decision Making
Introduction:
Financial management is a critical aspect of every organization, whether it’s a multinational corporation or a small startup. It encompasses the processes, tools, and techniques used to make informed financial decisions that align with the organization’s goals and objectives. In this blog post, we will explore the key concepts and functions of financial management, examining real-life examples from both a global and Indian perspective. Additionally, we will delve into case studies, numerical analysis, and practical applications to provide a comprehensive understanding of this crucial discipline.
Importance of Financial Management:
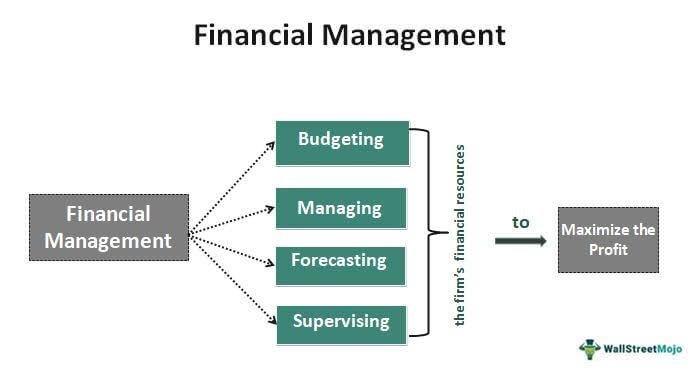
Financial management plays a pivotal role in an organization’s success. By effectively managing financial resources, a company can optimize profitability, mitigate risks, and make informed strategic decisions. From determining the cost of capital to evaluating investment opportunities and maintaining adequate working capital, financial management serves as the foundation for sound decision making. It ensures the efficient allocation of resources and maximizes shareholder wealth, ultimately contributing to sustainable growth and long-term success.
Key Concepts in Financial Management:
1. Time Value of Money:
The time value of money recognizes that a dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received in the future due to the opportunity cost of investing that money. We will explore the principles of compounding, discounting, and present value calculations, highlighting their significance in financial decision making.
2. Risk and Return:
Understanding the relationship between risk and return is vital for effective financial management. We will discuss various risk measurement techniques and explore how organizations assess and balance risk against potential returns to optimize their investment portfolios.
3. Cost of Capital:
The cost of capital represents the minimum return required by investors to compensate for the risk associated with a particular investment. We will examine the components of the cost of capital, such as the cost of debt and equity, and their impact on investment decisions and capital structure.
4. Capital Budgeting:
Capital budgeting involves evaluating and selecting investment projects that generate long-term value for the organization. We will explore popular capital budgeting techniques, including Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Payback Period, along with their applications in assessing project viability and profitability.
5. Financial Planning and Forecasting:
Financial planning involves setting goals, formulating strategies, and developing budgets to achieve desired financial outcomes. We will discuss the importance of financial planning and explore forecasting techniques, such as trend analysis and regression analysis, to make accurate predictions and guide decision making.
6. Working Capital Management:
Working capital management focuses on managing the company’s short-term assets and liabilities to ensure smooth operations and liquidity. We will explore strategies to optimize working capital, including inventory management, accounts receivable and payable management, and cash flow forecasting.
7. Capital Structure:
Capital structure refers to the mix of debt and equity financing used by a company to finance its operations and investments. We will examine various capital structure theories, such as Modigliani-Miller propositions, and discuss the implications of different capital structure decisions on the company’s risk and cost of capital.
8. Dividend Policy:
Dividend policy involves determining the proportion of earnings distributed to shareholders as dividends versus retained for reinvestment. We will explore different dividend policies, such as stable dividend policy and residual dividend policy, and analyze their impact on shareholder wealth and firm value.
Financial Management in the World Context:
4.1 Real-Life Examples: Amazon and Apple:
We will analyze how financial management practices have contributed to the success of global giants like Amazon and Apple. We will examine their financial strategies, investment decisions, capital allocation, and risk management approaches to gain insights into effective financial management in a global context.
4.2 Case Study: Tesla’s Financial Management Strategies:
By studying Tesla’s financial management strategies, we will explore how the company leveraged innovative financial techniques, such as raising capital through debt and equity, to drive its growth and disrupt the automotive industry. We will analyze Tesla’s financial statements and discuss key financial ratios to evaluate its performance.
4.3 Application of Financial Management in International Investments:
We will explore the challenges and opportunities associated with international investments and discuss how financial management principles help organizations navigate foreign exchange risks, political uncertainties, and cultural differences. Real-life examples of multinational corporations expanding into new markets will be discussed.
Financial Management in the Indian Context:
5.1 Real-Life Examples: Tata Group and Reliance Industries:
We will examine how financial management practices have shaped the success of renowned Indian conglomerates like Tata Group and Reliance Industries. We will explore their financial strategies, mergers and acquisitions, fundraising initiatives, and risk management approaches.
5.2 Case Study: Flipkart’s Financial Management Journey:
By analyzing the financial management journey of Flipkart, a leading Indian e-commerce company, we will highlight the importance of financial planning, capital infusion, and strategic partnerships in driving its growth. We will discuss the challenges faced by Flipkart and the financial decisions that led to its success.
5.3 Application of Financial Management in Indian Startups:
We will explore how financial management concepts are applied in the context of Indian startups. We will discuss fundraising options, valuation methods, financial modeling, and risk management strategies specifically tailored to the unique challenges faced by startups in India.
Numerical Analysis and Calculations:
6.1 Calculating Net Present Value (NPV):
We will walk through the process of calculating NPV and explain how it is used to evaluate investment projects. Through numerical examples, we will demonstrate the importance of discounting future cash flows and interpreting NPV results.
6.2 Assessing Return on Investment (ROI):
We will discuss the ROI metric and demonstrate how it can be used to assess the profitability and efficiency of investments. Real-life case studies and numerical examples will be provided to illustrate the calculation and interpretation of ROI.
6.3 Evaluating Working Capital Ratios:
We will explore various working capital ratios, such as current ratio, quick ratio, and cash conversion cycle, and explain how they are used to assess a company
‘s liquidity and operational efficiency. Through numerical analysis, we will demonstrate how to calculate and interpret these ratios.
6.4 Analyzing Financial Statements:
We will delve into the analysis of financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. We will discuss key financial ratios, such as profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and leverage ratios, and demonstrate their application through real-life examples and case studies.
The Role of Financial Management in Decision Making:
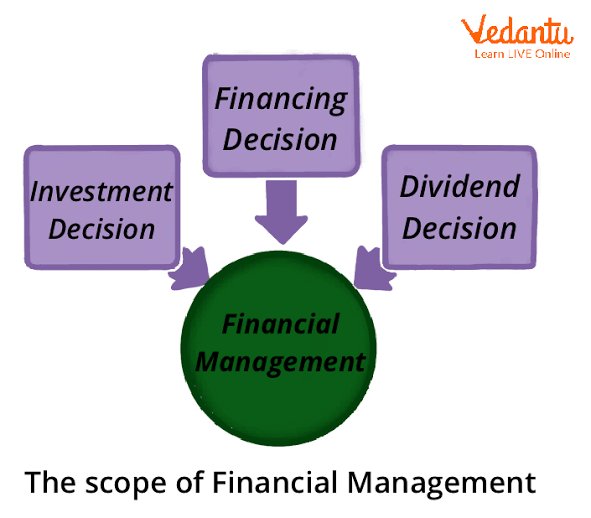
We will emphasize the crucial role of financial management in decision making across various organizational functions. From investment decisions to financing choices, risk management, and dividend policy, we will highlight how financial management concepts and techniques enable informed and strategic decision making that aligns with the organization’s goals and maximizes shareholder value.
Conclusion:
Financial management is an essential discipline that empowers organizations to make sound financial decisions, achieve sustainable growth, and create value for stakeholders. By understanding key concepts, analyzing real-life examples, and applying numerical analysis, organizations can navigate complex financial landscapes and optimize their financial resources. In both global and Indian contexts, financial management plays a pivotal role in shaping the success of companies across diverse industries.
Categories: Finance, Management, Financial Planning
Financial Management: Concepts and Functions for Effective Decision Making
Introduction:
Financial management is a critical aspect of every organization, whether it’s a multinational corporation or a small startup. It encompasses the processes, tools, and techniques used to make informed financial decisions that align with the organization’s goals and objectives. In this blog post, we will explore the key concepts and functions of financial management, examining real-life examples from both a global and Indian perspective. Additionally, we will delve into case studies, numerical analysis, and practical applications to provide a comprehensive understanding of this crucial discipline.
Importance of Financial Management:
Financial management plays a pivotal role in an organization’s success. By effectively managing financial resources, a company can optimize profitability, mitigate risks, and make informed strategic decisions. From determining the cost of capital to evaluating investment opportunities and maintaining adequate working capital, financial management serves as the foundation for sound decision making. It ensures the efficient allocation of resources and maximizes shareholder wealth, ultimately contributing to sustainable growth and long-term success.
Key Concepts in Financial Management:
1. Time Value of Money:
The time value of money recognizes that a dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received in the future due to the opportunity cost of investing that money. We will explore the principles of compounding, discounting, and present value calculations, highlighting their significance in financial decision making.
2. Risk and Return:
Understanding the relationship between risk and return is vital for effective financial management. We will discuss various risk measurement techniques and explore how organizations assess and balance risk against potential returns to optimize their investment portfolios.
3. Cost of Capital:
The cost of capital represents the minimum return required by investors to compensate for the risk associated with a particular investment. We will examine the components of the cost of capital, such as the cost of debt and equity, and their impact on investment decisions and capital structure.
4. Capital Budgeting:
Capital budgeting involves evaluating and selecting investment projects that generate long-term value for the organization. We will explore popular capital budgeting techniques, including Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Payback Period, along with their applications
in assessing project viability and profitability.
5. Financial Planning and Forecasting:
Financial planning involves setting goals, formulating strategies, and developing budgets to achieve desired financial outcomes. We will discuss the importance of financial planning and explore forecasting techniques, such as trend analysis and regression analysis, to make accurate predictions and guide decision making.
6. Working Capital Management:
Working capital management focuses on managing the company’s short-term assets and liabilities to ensure smooth operations and liquidity. We will explore strategies to optimize working capital, including inventory management, accounts receivable and payable management, and cash flow forecasting.
7. Capital Structure:
Capital structure refers to the mix of debt and equity financing used by a company to finance its operations and investments. We will examine various capital structure theories, such as Modigliani-Miller propositions, and discuss the implications of different capital structure decisions on the company’s risk and cost of capital.
8. Dividend Policy:
Dividend policy involves determining the proportion of earnings distributed to shareholders as dividends versus retained for reinvestment. We will explore different dividend policies, such as stable dividend policy and residual dividend policy, and analyze their impact on shareholder wealth and firm value.
Financial Management in the World Context:
4.1 Real-Life Examples: Amazon and Apple:
We will analyze how financial management practices have contributed to the success of global giants like Amazon and Apple. We will examine their financial strategies, investment decisions, capital allocation, and risk management approaches to gain insights into effective financial management in a global context.
4.2 Case Study: Tesla’s Financial Management Strategies:
By studying Tesla’s financial management strategies, we will explore how the company leveraged innovative financial techniques, such as raising capital through debt and equity, to drive its growth and disrupt the automotive industry. We will analyze Tesla’s financial statements and discuss key financial ratios to evaluate its performance.
4.3 Application of Financial Management in International Investments:
We will explore the challenges and opportunities associated with international investments and discuss how financial management principles help organizations navigate foreign exchange risks, political uncertainties, and cultural differences. Real-life examples of multinational corporations expanding into new markets will be discussed.
Financial Management in the Indian Context:
5.1 Real-Life Examples: Tata Group and Reliance Industries:
We will examine how financial management practices have shaped the success of renowned Indian conglomerates like Tata Group and Reliance Industries. We will explore their financial strategies, mergers and acquisitions, fundraising initiatives, and risk management approaches.
5.2 Case Study: Flipkart’s Financial Management Journey:
By analyzing the financial management journey of Flipkart, a leading Indian e-commerce company, we will highlight the importance of financial planning, capital infusion, and strategic partnerships in driving its growth. We will discuss the challenges faced by Flipkart and the financial decisions that led to its success.
5.3 Application of Financial Management in Indian Startups:
We will explore how financial management concepts are applied in the context of Indian startups. We will discuss fundraising options, valuation methods, financial modeling, and risk management strategies specifically tailored to the unique challenges faced by startups in India.
Numerical Analysis and Calculations:
6.1 Calculating Net Present Value (NPV):
We will walk through the process of calculating NPV and explain how it is used to evaluate investment projects. Through numerical examples, we will demonstrate the importance of discounting future cash flows and interpreting NPV results.
6.2 Assessing Return on Investment (ROI):
We will discuss the ROI metric and demonstrate how it can be used to assess the profitability and efficiency of investments. Real-life case studies and numerical examples will be provided to illustrate the calculation and interpretation of ROI.
6.3 Evaluating Working Capital Ratios:
We will explore various working capital ratios, such as current ratio, quick ratio, and cash conversion cycle, and explain how they are used to assess a company’s liquidity and operational efficiency. Through numerical analysis, we will demonstrate how to calculate and interpret these ratios.
6.4 Analyzing Financial Statements:
We will delve into the analysis of financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. We will discuss key financial ratios, such as profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and leverage ratios, and demonstrate their application through real-life examples and case studies.
The Role of Financial Management in Decision Making:
We will emphasize the crucial role of financial management in decision making across various organizational functions. From investment decisions to financing choices, risk management, and dividend policy, we will highlight how financial management concepts and techniques enable informed and strategic decision making that aligns with the organization’s goals and maximizes shareholder value.
Conclusion:
Financial management is an essential discipline that empowers organizations to make sound financial decisions, achieve sustainable growth, and create value for stakeholders. By understanding key concepts, analyzing real-life examples, and applying numerical analysis, organizations can navigate complex financial landscapes and optimize their financial resources. In both global and Indian contexts, financial management plays a pivotal role in shaping the success of companies across diverse industries.
Categories: Finance, Management, Financial Planning
Leave a comment