

Introduction:
Welcome to our blog on performance appraisal methods! In today’s dynamic and competitive business world, evaluating and assessing employee performance is crucial for organizational success. Effective performance appraisal methods help organizations identify strengths, areas for improvement, and align individual goals with organizational objectives. In this article, we will explore various performance appraisal methods, provide real-life examples, and delve into case studies from both global and Indian contexts.
Table of Contents:
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Performance Appraisal Methods
2.1 Graphic Rating Scale
2.2 Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS)
2.3 Management by Objectives (MBO)
2.4 360-Degree Feedback
2.5 Forced Ranking
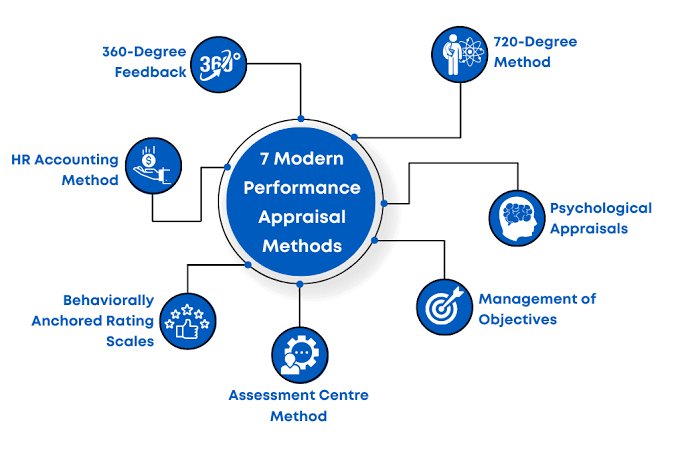
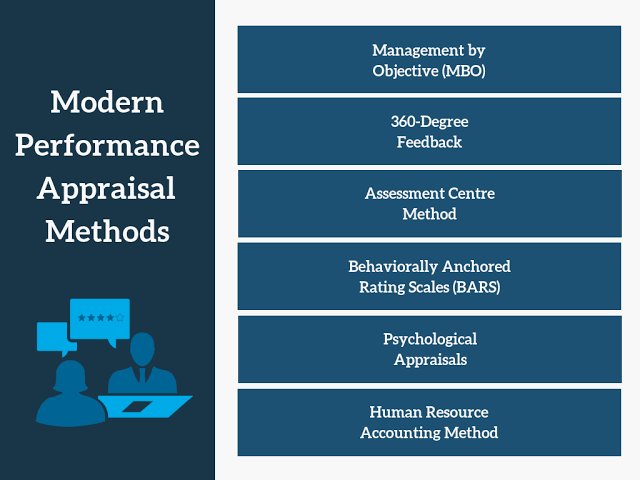
3. Modern Performance Appraisal Methods
3.1 Critical Incident Technique (CIT)
3.2 Continuous Performance Management
3.3 Performance Scorecards
3.4 Behavioral Observation Scales (BOS)
3.5 Peer Evaluation
4. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
4.1 Example 1: XYZ Corporation’s Implementation of Graphic Rating Scale
4.2 Example 2: Google’s Approach to 360-Degree Feedback
4.3 Case Study 1: TATA Group’s Adoption of Management by Objectives
4.4 Case Study 2: Zappos’ Implementation of Continuous Performance Management
5. Performance Appraisal in the Indian Context
5.1 Performance Appraisal Practices in Indian Companies
5.2 Case Study 3: Infosys’ Performance Appraisal Transformation
5.3 Case Study 4: Mahindra & Mahindra’s Implementation of Behavioral Observation Scales
6. Conclusion
Traditional Performance Appraisal Methods:
1. Graphic Rating Scale:
The graphic rating scale method involves evaluating employees based on predefined criteria and assigning numerical ratings. For example, a salesperson could be assessed on their communication skills, sales targets, and customer service abilities.
2. Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS):
BARS involves defining specific behavioral indicators for each performance level and using them as a reference point during evaluations. This method provides clearer feedback and reduces subjectivity.
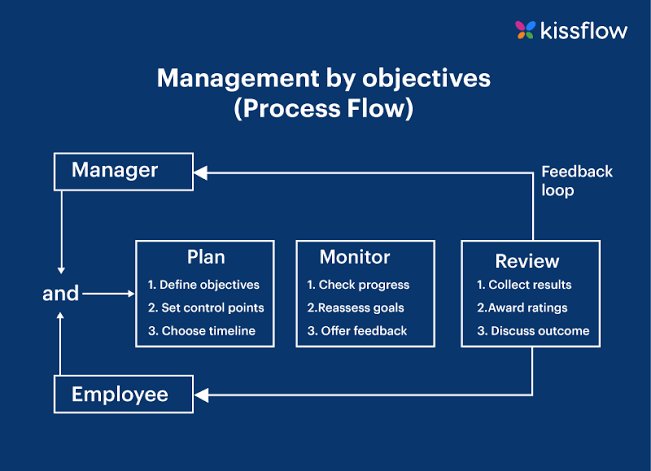
3. Management by Objectives (MBO):
MBO emphasizes setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals and then evaluating employees based on their ability to meet those objectives. It encourages collaboration and goal alignment between employees and managers.
4. 360-Degree Feedback:
This method gathers feedback from multiple sources, such as supervisors, peers, subordinates, and even customers. It provides a holistic view of an employee’s performance and helps identify blind spots.
5. Forced Ranking:
Forced ranking, also known as the “rank and yank” approach, involves categorizing employees into predetermined performance categories. While it can create healthy competition, it has faced criticism for its potential negative impact on morale.
Modern Performance Appraisal Methods:
1. Critical Incident Technique (CIT):
CIT involves identifying critical incidents where employees performed exceptionally well or poorly. These incidents serve as specific examples for feedback and development discussions.
2. Continuous Performance Management:
Continuous performance management focuses on ongoing feedback, coaching, and goal setting throughout the year. It fosters real-time communication and development, replacing annual reviews with frequent check-ins.
3. Performance Scorecards:
Performance scorecards measure performance against predefined objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs). They provide a visual representation of an employee’s progress towards their goals.
4. Behavioral Observation Scales (BOS):
BOS involves evaluating employees based on specific
observable behaviors linked to job performance. This method allows for objective assessment and helps identify areas for improvement.
5. Peer Evaluation:
Peer evaluation involves gathering feedback from colleagues and team members. It promotes teamwork, collaboration, and a broader perspective on an employee’s performance.
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies:
Example 1: XYZ Corporation’s Implementation of Graphic Rating Scale:
XYZ Corporation implemented a graphic rating scale to assess employee performance. This method allowed managers to evaluate employees on various criteria, such as teamwork, leadership, and problem-solving skills. The ratings helped identify top performers and those in need of further development.
Example 2: Google’s Approach to 360-Degree Feedback:
Google utilizes a comprehensive 360-degree feedback system to assess employee performance. By gathering feedback from multiple sources, including peers, managers, and subordinates, Google gains valuable insights into an employee’s strengths and areas for growth. Example 3: Amazon’s Utilization of Behavioral Anchored Rating Scales (BARS):
Amazon employs Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS) to evaluate employee performance. This method provides a detailed assessment of specific behaviors and competencies required for each role. For instance, an Amazon warehouse worker may be evaluated on their efficiency in order processing, adherence to safety protocols, and customer service skills.
Example 4: Microsoft’s Implementation of 360-Degree Feedback:
Microsoft utilizes a robust 360-degree feedback process to evaluate employee performance. Through anonymous surveys, employees receive feedback from supervisors, peers, direct reports, and even external stakeholders. This comprehensive approach enhances self-awareness, facilitates targeted development plans, and strengthens overall performance.
Case Study 1: TATA Group’s Adoption of Management by Objectives:
The TATA Group, a prominent Indian conglomerate, adopted the management by objectives approach. By setting clear and measurable goals, employees aligned their efforts with the organization’s strategic objectives, resulting in improved performance and increased employee satisfaction.
Case Study 2: Zappos’ Implementation of Continuous Performance Management:
Zappos, an e-commerce giant, implemented continuous performance management. The company replaced annual performance reviews with regular check-ins and feedback sessions, resulting in enhanced employee engagement, development, and alignment with company goals.
Performance Appraisal in the Indian Context:
In the Indian context, performance appraisal practices vary across organizations. Companies often combine traditional and modern methods to suit their specific needs. Case Study 3 focuses on Infosys, which transformed its performance appraisal process to include more frequent feedback and coaching, resulting in increased employee motivation and performance.
Case Study 4 explores Mahindra & Mahindra’s implementation of Behavioral Observation Scales, which provided a structured framework for evaluating employees’ observable behaviors. This approach improved transparency, fairness, and accuracy in performance assessments. Case Study 5: Accenture’s Adoption of Continuous Performance Management:
Accenture, a global professional services firm, embraced Continuous Performance Management (CPM). By replacing traditional annual appraisals with regular check-ins and real-time feedback, Accenture created a more agile and responsive performance management system. This shift led to increased employee engagement, improved goal alignment, and a culture of continuous learning. Case Study 6: HDFC Bank’s Application of Forced Ranking:
HDFC Bank, one of India’s leading banks, implemented a forced ranking system to evaluate employee performance. Through this method, employees were classified into distinct performance categories, such as top performers, average performers, and underperformers. This ranking system enabled the bank to identify high-potential individuals for career progression and implement targeted development plans. Case Study 7: Adobe’s Implementation of Peer Evaluation:
Adobe introduced peer evaluation as a key component of its performance appraisal process. Employees at Adobe provide feedback and evaluate their colleagues based on teamwork, collaboration, and contributions to the team’s success. This approach fosters a culture of transparency, encourages collaboration, and supports employee development. Case Study 8: Infosys’s Performance Appraisal Transformation:
Infosys, a prominent Indian IT services company, transformed its performance appraisal process to emphasize continuous feedback and coaching. The company implemented a cloud-based platform for real-time feedback exchange and encouraged managers to have frequent performance conversations with their team members. This shift resulted in higher employee engagement, improved performance, and a more agile feedback culture. Conclusion:
Performance appraisal methods play a vital role in assessing and improving employee performance. By implementing effective appraisal methods, organizations can motivate employees, align their efforts with strategic goals, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. This blog highlighted traditional and modern performance appraisal methods, accompanied by real-life examples and case studies from global and Indian contexts. By leveraging these methods, organizations can maximize employee potential, drive growth, and achieve long-term success.
https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-3482330748000937
Leave a comment