**Introduction**
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, organizations rely heavily on the collective efforts of their employees to achieve success. The behavior and dynamics of groups within an organization play a crucial role in determining its overall performance. Understanding group behavior and dynamics is essential for effective leadership, team building, and organizational success. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of group behavior, delve into group dynamics, and examine their significance in organizational behavior. We will also provide real-life examples and case studies to illustrate key concepts and offer valuable insights.
**Index**
1. Introduction
2. Definition of Group Behavior
3. Importance of Group Behavior in Organizational Behavior
4. Factors Influencing Group Behavior
– Communication
– Leadership
– Diversity
– Group Size
5. Types of Group Behavior
– Task-Oriented Behavior
– Relationship-Oriented Behavior
– Self-Oriented Behavior
6. Group Dynamics
7. Stages of Group Development
– Forming
– Storming
– Norming
– Performing
– Adjourning
8. Challenges in Group Dynamics
– Conflict Resolution
– Decision Making
– Power Struggles
9. Strategies for Enhancing Group Dynamics
– Effective Communication
– Encouraging Collaboration
– Building Trust
10. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
11. Conclusion
**Definition of Group Behavior**
Group behavior refers to the patterns of behavior exhibited by individuals when they interact within a group setting. It involves the study of how individuals behave, communicate, and influence one another within a group context. Group behavior encompasses various aspects, including decision-making, conflict resolution, leadership dynamics, and the overall functioning of the group.
**Importance of Group Behavior in Organizational Behavior**
Understanding group behavior is crucial for organizational success. Effective group behavior can lead to improved problem-solving, creativity, and innovation. It enhances communication and collaboration among team members, fostering a positive work environment. Furthermore, group behavior influences employee motivation, job satisfaction, and overall organizational performance. By recognizing and managing group dynamics effectively, organizations can harness the collective potential of their teams and achieve their goals.
**Factors Influencing Group Behavior**
Several factors influence group behavior within an organization. Let’s explore some of the key factors:
1. Communication: Open and effective communication is vital for successful group behavior. Clear communication channels facilitate the sharing of ideas, feedback, and information, fostering a collaborative environment.
2. Leadership: The leadership style within a group significantly impacts its behavior. Effective leaders inspire and motivate team members, set clear goals, and provide guidance. They encourage active participation and ensure that each member’s strengths are utilized.
3. Diversity: Group behavior is influenced by the diversity of its members. Diversity brings together individuals with different perspectives, skills, and experiences, leading to enhanced creativity and problem-solving. However, managing diversity also requires sensitivity and inclusivity.
4. Group Size: The size of a group affects its behavior. Smaller groups tend to have higher levels of participation, better communication, and faster decision-making. Large groups, on the other hand, may experience challenges in coordination and individual engagement.
**Types of Group Behavior**
Group behavior can be categorized into three main types:
1. Task-Oriented Behavior: This type of behavior focuses on accomplishing specific tasks or goals. It involves planning, organizing, and coordinating efforts to achieve desired outcomes.
2. Relationship-Oriented Behavior: Relationship-oriented behavior emphasizes building and maintaining positive relationships within the group. It involves fostering trust, mutual respect, and support among team members.
3. Self-Oriented Behavior: Self-oriented behavior refers to actions driven by individual motives and
self-interest. It may include behaviors such as seeking personal recognition, prioritizing individual goals over group goals, or engaging in competitive behaviors.
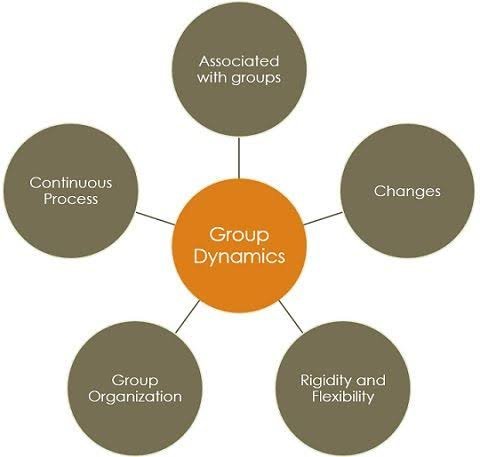
**Group Dynamics**
Group dynamics refers to the patterns of interaction, influence, and relationships among group members. It encompasses the complex interplay of individual personalities, roles, norms, and power dynamics within a group. Understanding group dynamics is essential for predicting and managing group behavior effectively.
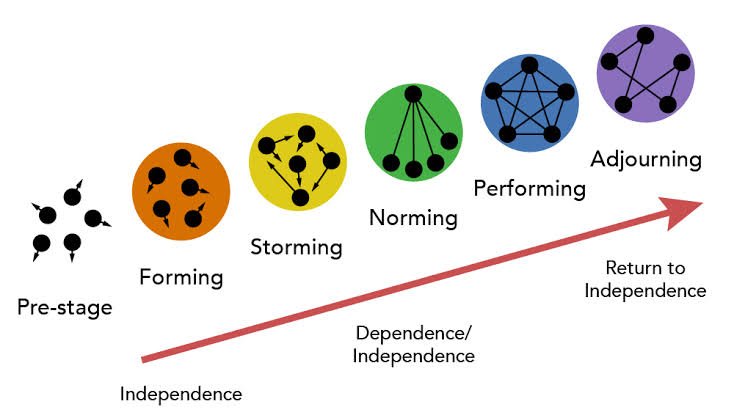
**Stages of Group Development**
Groups typically go through several stages of development. Let’s explore these stages:
1. Forming: In this initial stage, group members come together, get acquainted, and establish initial relationships. There is a focus on understanding the group’s purpose, goals, and individual roles.
2. Storming: During this stage, conflicts, power struggles, and differences of opinion may arise as group members establish their positions within the group. It is essential to address these challenges effectively to move forward.
3. Norming: In the norming stage, the group establishes norms, values, and acceptable behavior patterns. Group cohesion and trust begin to develop as members align their efforts towards common goals.
4. Performing: The performing stage is characterized by high levels of cooperation, collaboration, and productivity. The group functions as a cohesive unit, and members work together effectively to achieve desired outcomes.
5. Adjourning: In the final stage, the group disbands either due to the completion of the task or a change in organizational circumstances. This stage allows for reflection and evaluation of the group’s accomplishments and challenges.
**Challenges in Group Dynamics**
While group dynamics can be highly beneficial, they can also present challenges that need to be addressed:
1. Conflict Resolution: Conflicts within a group can hinder progress and create tension. Effective conflict resolution strategies, such as open communication, active listening, and mediation, are essential for maintaining a positive group dynamic.
2. Decision Making: Group decision making can be complex, especially when multiple perspectives and interests are involved. Ensuring a fair and inclusive decision-making process that considers diverse viewpoints is crucial for maintaining group cohesion.
3. Power Struggles: Power dynamics can emerge within a group, leading to internal conflicts and a lack of cooperation. Encouraging shared leadership and promoting equal participation can help mitigate power struggles and foster a more collaborative environment.
**Strategies for Enhancing Group Dynamics**
To promote positive group dynamics, organizations can adopt the following strategies:
1. Effective Communication: Encouraging open and transparent communication channels enables the exchange of ideas, concerns, and feedback. Regular team meetings, collaborative platforms, and active listening foster a culture of effective communication.
2. Encouraging Collaboration: Promoting collaboration and teamwork enhances group dynamics. Assigning tasks that require interdependence, fostering a sense of shared responsibility, and recognizing and valuing individual contributions can strengthen collaboration.
3. Building Trust: Trust is the foundation of positive group dynamics. Building trust involves promoting honesty, transparency, and accountability within the group. Encouraging constructive feedback, honoring commitments, and recognizing achievements can contribute to trust-building.
**Real-Life Examples and Case Studies**
1. Example: XYZ Corporation implemented a team-based approach for a complex project. By leveraging diverse skills and fostering effective communication and collaboration, the team achieved project milestones ahead of schedule, leading to increased client satisfaction and overall success.
2. Case Study: In a multinational organization, a cross-functional team faced challenges due to cultural differences and conflicting priorities. Through cultural sensitivity training, open dialogue, and shared goal setting, the team overcame barriers and improved collaboration, resulting in higher productivity and innovation.
**Conclusion**
Group behavior and dynamics significantly influence the functioning and performance of organizations. Understanding the complexities of group behavior, recognizing the various stages of group development, and addressing challenges effectively are essential for creating a positive work environment and achieving organizational goals.
https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-3482330748000937
Leave a comment