

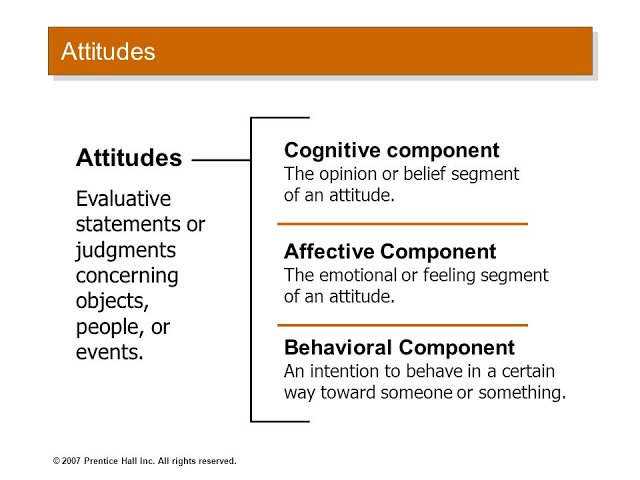
Introduction:
Attitude plays a crucial role in shaping the behavior and performance of individuals within an organization. It influences how employees perceive their work, interact with colleagues, and approach tasks and challenges. In this blog post, we will explore various theories of attitude in organizational behavior and provide real-life examples and case studies to illustrate their practical application. Whether you are a manager, a team leader, or an employee, understanding these theories can help you create a positive work environment and enhance organizational effectiveness.
Index:
1. Introduction
2. Theories of Attitude in Organizational Behavior
2.1 Cognitive Dissonance Theory
2.2 Social Learning Theory
2.3 Self-Perception Theory
2.4 Affective Events Theory
3. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
3.1 Attitude and Employee Motivation
3.2 Attitude and Organizational Culture
3.3 Attitude and Customer Service
4. Conclusion
5. References
Category: Organizational Behavior
Theories of Attitude in Organizational Behavior:
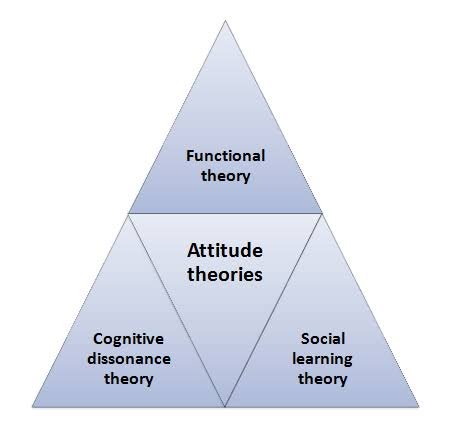
1. Cognitive Dissonance Theory:
The cognitive dissonance theory suggests that individuals strive to maintain consistency between their attitudes and behaviors. When there is a discrepancy between the two, it creates a state of discomfort known as cognitive dissonance. For example, if an employee strongly believes in the importance of work-life balance but consistently works overtime, they may experience cognitive dissonance. Managers can address this by promoting policies that align with employees’ attitudes and values, such as flexible work hours or remote work options.
2. Social Learning Theory:
The social learning theory proposes that individuals acquire attitudes through observation, imitation, and reinforcement. Employees are more likely to adopt attitudes exhibited by their role models or influential colleagues. For instance, if a team leader consistently demonstrates a positive and respectful attitude towards team members, it is likely to influence the attitudes of other team members positively. To leverage this theory, organizations should encourage positive role modeling and provide opportunities for employees to observe and learn from exemplary attitudes.
3. Self-Perception Theory:
According to the self-perception theory, individuals develop their attitudes by observing their own behavior and inferring their attitudes based on that behavior. For example, if an employee consistently volunteers for challenging projects, they may perceive themselves as someone who enjoys taking risks and seeking growth opportunities. Organizations can utilize this theory by providing employees with opportunities to engage in tasks aligned with positive attitudes, fostering a sense of competence and job satisfaction.
4. Affective Events Theory:
The affective events theory suggests that specific events or incidents in the workplace can trigger emotional responses that influence an individual’s attitude. These emotional experiences can be positive or negative, affecting job satisfaction, commitment, and overall well-being. For instance, recognition and rewards for exceptional performance can generate positive emotions and foster a positive attitude among employees. Organizations can proactively create a supportive and positive work environment to minimize negative events and maximize positive experiences.
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies:
3.1 Attitude and Employee Motivation:
Case Study: XYZ Corporation implemented a reward and recognition program to motivate employees. By acknowledging employees’ achievements and efforts publicly, they created a positive emotional impact and reinforced a sense of pride and satisfaction among the workforce. As a result, employees displayed increased motivation, productivity, and a more positive attitude towards their work.
3.2 Attitude and Organizational Culture:
Case Study: ABC Corporation developed a strong organizational culture centered around open communication and collaboration. By fostering an environment that values employees’ opinions and encourages teamwork, they nurtured a positive attitude among employees. This positive attitude translated into enhanced creativity, innovation, and a shared commitment to organizational goals.
3.3 Attitude and Customer Service:
Case Study: The customer service department at XYZ Bank implemented a customer-centric attitude as part of their organizational culture. They trained their employees to maintain a positive and empathetic attitude towards customers, even in challenging situations. This approach resulted in improved customer satisfaction, increased customer loyalty, and positive word-of-mouth referrals. The positive attitude of the employees created a favorable impression of the bank and strengthened its reputation in the market.
Conclusion:
Attitude plays a significant role in shaping organizational behavior and outcomes. By understanding and applying theories of attitude in organizational behavior, managers and leaders can create a positive work environment, enhance employee motivation, and improve overall organizational effectiveness. The examples and case studies provided in this blog highlight the practical application of attitude theories in real-life situations. By fostering positive attitudes among employees, organizations can achieve higher levels of employee engagement, customer satisfaction, and long-term success.
Leave a comment