
Introduction:
Demand analysis is a fundamental concept in economics that helps businesses understand consumer behavior and make informed decisions. By analyzing factors such as utility, indifference curves, elasticity, and forecasting, businesses can gain insights into customer preferences and effectively plan their marketing strategies. In this blog post, we will explore these key components of demand analysis in easy-to-understand language.
Utility Analysis:
Utility refers to the satisfaction or benefit that individuals derive from consuming goods or services. Utility analysis aims to measure and quantify this satisfaction. Economists use the concept of utils to represent the level of utility. By understanding the utility derived from different goods or services, businesses can gauge consumer preferences and make strategic decisions regarding product features, pricing, and marketing campaigns.
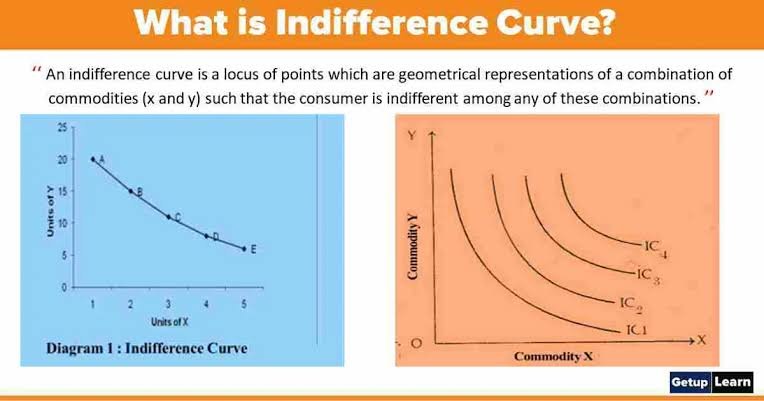
Indifference Curve:
An indifference curve is a graphical representation that shows different combinations of goods or services that provide an equal level of utility to consumers. It illustrates the concept of consumer preferences and trade-offs. The shape of an indifference curve reveals the consumer’s willingness to substitute one good for another while maintaining the same level of satisfaction. Businesses can analyze indifference curves to identify consumer preferences and design product bundles that cater to their target market’s needs.
Elasticity:
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of demand to changes in price, income, or other relevant factors. Understanding elasticity is crucial for businesses to set pricing strategies and estimate the impact of price changes on demand. Price elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in quantity demanded relative to a percentage change in price. If demand is elastic, a small price change can significantly affect the quantity demanded, while inelastic demand indicates a smaller response to price changes. By considering elasticity, businesses can optimize pricing decisions and revenue generation.
Forecasting:
Demand forecasting involves estimating future consumer demand for a particular product or service. It helps businesses plan production, inventory management, marketing campaigns, and resource allocation. Various methods, such as time series analysis, statistical modeling, and market research, are used to forecast demand. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and external factors, businesses can anticipate fluctuations in demand and make informed decisions to meet customer needs effectively.
Conclusion:
Demand analysis provides valuable insights into consumer behavior and preferences, enabling businesses to make strategic decisions. By employing utility analysis, indifference curves, elasticity, and demand forecasting techniques, businesses can understand consumer preferences, set optimal prices, design effective marketing strategies, and plan for the future. A thorough understanding of demand analysis empowers businesses to stay competitive, meet customer needs, and achieve their goals.
Categories: Demand Analysis, Utility Analysis, Indifference Curve, Elasticity, Forecasting.
Leave a comment